Ear pain is not uncommon. This happens not only to healthy people but also in patients with underlying diseases. Ear pain is often accompanied additional symptoms. This article will tell you why your ears hurt, how to treat this trouble.
Ear pain is the cause
Ear pain can be shooting, pressing or aching. Only making the correct diagnosis, that is, finding out the real cause, will help you choose the right treatment and get rid of this ailment.
Unpleasant sensations in the auricle in healthy people can occur as a result of:
- increased sensitivity to cold and wind;
- violation of personal hygiene, an excessive amount of sulfur leads to discomfort;
- violation of intra-ear pressure, for example, when landing an airplane or scuba diving.
Remember that you can cope with a change in pressure in the ear by making chewing and swallowing movements. You can also try pinching your nose with two fingers and exhaling forcefully.
Another pain in the ear occurs with the ear diseases themselves. Such as:
- Otitis.
- Mastoiditis.
- Tumors.
- Physical injury.
And a list of diseases that manifest themselves as ear pain, but in reality are a disease of a completely different nature:
- dental diseases - pulpitis, caries;
- inflammation in the throat, for example, the tonsils hurt, the larynx is swollen;
- consequences of trauma in the temporal-maxillary part of the face;
- sinusitis;
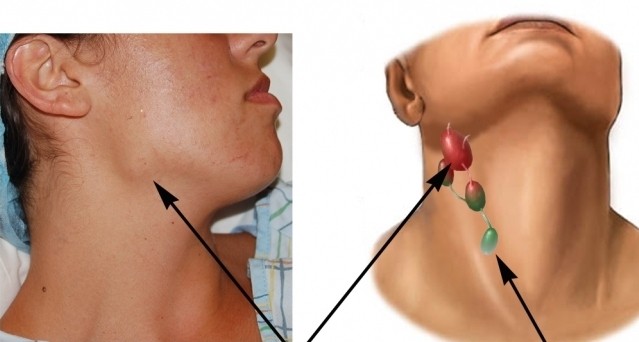
- inflammation of the ear lymph node;
- mumps;
- foreign body;
- bathing in polluted waters;
- swelling of the salivary gland located near the ear;
- pinching of the cervical spine;
- irritation of the trigeminal or glossopharyngeal nerves;
- arthritis;
- tumors inside the skull.
As you can see, ear pain can be fraught with quite serious ailments, the neglect of which can be extremely dangerous for health and life. Plus, ear pain brings tangible discomfort. It shouldn't be tolerated. Seek medical attention as soon as possible.
Ear pain - symptoms
Pain in the auricle can go in the company of discomfort in another organ. What are these sensations and what do they indicate? Ear pain, in association with:
- talking about jumps blood pressure. Often accompanied by noise or ringing in the ears, a rush of blood to the face, flies or spots before the eyes. In this case, it is necessary to immediately call the doctors, for a speedy, but careful pressure reduction.
- Toothache. What indicates the presence of an inflammatory process in the tooth. The trigeminal nerve connects the ear canal and the teeth, so pain is felt in both places at the same time. Do not postpone a visit to the doctor, because dental diseases can develop into pulpitis or flux.
- Pain when eating. Most likely this is the beginning of a sore throat or otitis media.
Ear pain radiates to throat
More precisely, with chewing and swallowing movements. As a rule, these are satellites of otitis media. They can also talk about the onset of mumps, tonsillitis, pharyngitis, inflammatory processes in the cervical region, diseases of the larynx and mouth. This is explained by the fact that the trigeminal nerve connects the ear apparatus and the nasopharynx. A more specific history can only be given by a specialist, after a thorough examination.
Usually, pains of this nature are accompanied by general weakness, drowsiness, loss. In especially severe cases of diseases, there may be an increase in body temperature up to 40 degrees and the release of fluid from the auricle. For example, purulent otitis. Often, pain in the throat and ear at the same time, accompanied by an infectious disease. You should not postpone a visit to a specialist if you do not want to get complications.
With acute pain in the ear canal, the use of painkillers is allowed. For example, Nurafen, Paracetamol, Next, Pentalgin. It does not hurt to sanitize the oral cavity and larynx with a disinfectant solution. For example, Miramistin, hydrogen peroxide with water, calendula tincture in an aqueous solution. Or just decoction medicinal herbs. Such as chamomile, calendula, sage.
Ear pain radiates to jaw

In addition to the ailments described above, pain of this type may also indicate other diseases. For example:
- "red ear" syndrome, it is caused by neuralgia, damage to the thalamus, disruption of the jaw joint;
- a wisdom tooth grows, accompanied by headaches and a general deterioration in well-being;
- stiffening or pinching of the trigeminal nerve;
- special forms of arthritis, accompanied by fever and difficulty opening the mouth;
- malocclusion, pain occurs with increased stress;
- migraine;
- wearing braces, it is believed that such pain is a good sign, which means that the correction process is in full swing;
- tumors in the neck, squeezing the carotid artery.
Severe ear pain

If the probability of injury is excluded, then most likely we will talk about the inflammatory process. The pain is sharp, shooting. Most likely, these are severe forms of otitis media - purulent or catarrhal. May be accompanied by ear fluid, fever, ear swelling, and tinnitus. It is usually the result of a viral illness. In no case do not self-medicate. Seek professional help as soon as possible. They will prescribe ear drops and antibiotics. They will also prescribe pain medication.
First aid to a person of any age in this case consists in the following actions:
- Drip vasoconstrictor drops into the nose. Even if there is no cold. This is done to reduce internal pressure.
- Take any pain medication that is allowed. Children from 3 months can be given 2.5 ml of Nurofen syrup.
Ear pain - treatment

First of all, you need to make sure that the disease is not aggravated by an abscess or infection. This can only be clarified by a specialist. First aid for ear pain - dry heat. Do not forget that heat can accelerate the spread of infection, if any.
The use of painkillers is allowed. The doctor may prescribe ear drops. Medicines for the treatment of ear pain are divided into:
- Vasoconstrictor, relieve swelling.
- With an antibiotic to eliminate the inflammatory process.
- Alcohol compresses.
- Antiallergic agents.
- Antiseptics.
- Ear candles.
- Medications to dissolve sulfuric plug.
- Antivirals.
- Ointments and traditional medicine.
The use of traditional medicine for the treatment of ear pain is possible strictly after diagnosis. Since many home remedies are based on heating the auricle, this is not always acceptable. Especially in the presence of elevated body temperature.
If the otolaryngologist has given permission, then you can be treated both by applying heat to the sore ear, and by instilling special products made from natural products at home.
Feeling pain in the ear, or already undergoing therapy to eliminate it, in no case should you:
- go out with open ears, put on a hat, wrap yourself in a scarf;
- independently climb into the ear canal with various objects or dirty hands;
- rinse the ear with a strong jet;
- do not carry out timely sanitation of the ear canal;
- use a medicine not prescribed by a doctor, especially when combined with a prescribed medication;
- heat the ear too often and too much.
Folk remedies for ear pain
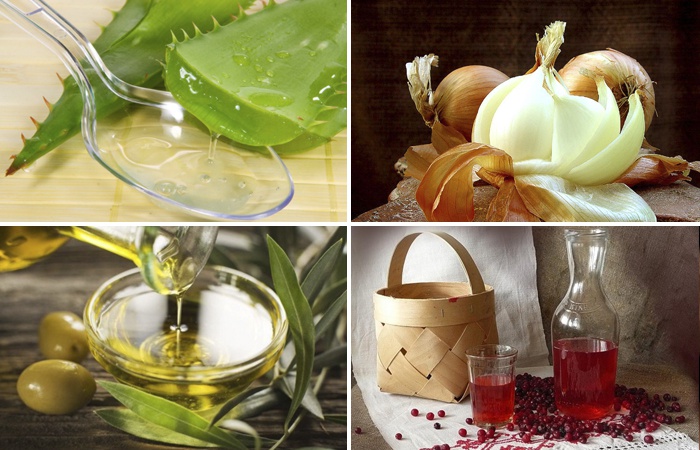

Do not forget that you can start self-treatment only after making a diagnosis. Not all ailments accompanied by pain in the ear benefit from heat. ethnoscience offers a wide range of ear pain remedies. We suggest you familiarize yourself with the most effective recipes of traditional medicine.
- Heated olive oil. Moisturizes the ear canal and fights inflammation. Enough 3-4 drops of warm oil in sore ear.
- Onion or garlic juice. It has excellent antiseptic properties. Drip 2-3 drops of juice, 3 times a day.
- Ginger extract mixed with olive oil.
- Essential oil of mint or basil. Relieves acute pain.
- Camphor oil. It can be dripped into a sore ear, or used as a warming compress. Take the gauze folded in several layers and cut a hole for the sink on it. Then soak in warm camphor oil and apply to the sore spot.
- Hydrogen peroxide is well suited for gentle cleaning of ear wax and has antimicrobial properties.
- Bury room geranium juice in your ear.
- Alcohol tincture of calendula or propolis. Dilute with water in equal proportions. Apply both for instillation inside and as part of compresses.
- Boric alcohol. Works well for acute pain. Soak a cotton swab in alcohol and insert into your ear. Prohibited for use in children.
- Almond oil, wormwood decoction, glycerin or bay leaf decoction. Any means is good. Bury 2-3 drops in the ear.
Remember that any compress can be kept for no more than 4 hours.
Ear congestion without pain

If the ears are blocked, but there is no severe pain, then the problem may be as follows:
- getting excess moisture into the auditory opening, for example, when bathing;
- pressure drop observed during takeoff and landing of the aircraft;
- poor sanitation of the auditory canal, the presence of a sulfur plug in it;
- inflammation of the auditory tube, most often occurs in parallel with acute respiratory infections.
If mortgages occur periodically and for a short time, then there is no concern. You can almost always deal with it yourself. For example, to normalize the internal pressure in the ear, you need to chew gum. Excess moisture must be carefully collected with a cotton swab. Or tilt your head so that the liquid flows out by itself. Please note that excessive hygiene in the ear canal is also not good. Not a large number of earwax is necessary to prevent bacteria from multiplying.
If unpleasant sensations occur frequently, and their duration causes tangible discomfort, this is a reason to visit an otolaryngologist.
Child's ear hurts

In children aged 3-6 years, due to the peculiarities of the structure of a fragile organism, otitis media can occur regularly. It appears suddenly, with sharp pain and fever. In infants, it may be accompanied by vomiting, diarrhea. For children under 2 years of age, the use of any ear drops is contraindicated, only the use of compresses is permissible. Also, children under 2 years of age rely on antibiotics. Older babies are allowed to bring down the temperature only if it is above 38 degrees.
First aid for a child with acute pain in the ear is the same as for an adult - vasoconstrictor drops in the nose and a dose of paracetamol-containing drug. Most often it is Ibuprofen or Nurofen. Do not be nervous and panic. All children get sick, and your nerves will not help the cause. Keep a cool mind, your child needs you. Do not forget to provide the patient with complete rest and increased care. Do not forcefully try to put a compress on the baby. Every touch hurts.
Child has earache and fever

The most harmless dressing in case of acute ear pain is to put a clean, dry piece of cotton wool on the ear, cover it with a bag and wrap it with a scarf. This method will not give a strong warming effect, but it will save you from external influences.
Remember that in childhood, any products containing alcohol or salicylic acid are prohibited for use. Due to their high toxicity to a fragile organism. It is allowed to apply dry heat only at the first complaints of pain. If this does not help, the pain intensifies, the temperature rises or discharge from the auricle appears - stop any independent actions and call an ambulance.
The child has an earache - what to do

For more information on first aid for a child with earache and what to do in case of a child's pain, see above.
If your baby has been prescribed ear drops that are only suitable for children over 2 years old, read the instructions on how to bury them correctly.
- All drops, compresses and other means for treatment must be warm. If the drops are stored in the refrigerator, place the vial in hot water for a few minutes. Then check on your hand the comfort of their temperature.
- The baby should lie on its side. Only in this position will the drops reach their destination. In this case, it is recommended to slightly pull the sink. Babies - back and down. For older children, back and up
- After instillation, you need to lie down quietly for several minutes. Many drops have an oily texture and take time to penetrate into the ear canal.
- Do not exceed the dose. This treatment is unlikely to speed up, but an overdose can lead to side effects.
The winter that has come again resembles a windy young girl. Severe frosts constantly alternate with warming. There is an irresistible desire to get rid of annoying warm clothes and take a deep breath. After all, the air is so clean and pleasant. But you should be careful. Since such a thaw can threaten the occurrence of various colds.
Immediately the next day after such a walk in winter time may cause pain in the ear area. Such pain often passes into. Only in rare cases, patients go to the doctor for help, and so we are used to treating ourselves. It's easier to go to the pharmacy and ask the pharmacist to advise us something for pain. We drink pills, do washings and many other procedures.
The danger of all this lies in the fact that having made a diagnosis for ourselves, in fact, we have no idea about the possible complexity of the disease. Therefore, the treatment should be different. As often happens, we begin to solve a completely different problem. But this is our health and we should not forget about it. And without suspecting, we cripple ourselves. The disease proceeds to another stage and then it will be more difficult to cope with it. Even an experienced doctor can find himself in a quandary after such self-treatment. In this case, you should not waste time and determine the correct diagnosis of the disease. It can be an inflammation of the ear (otitis media), a bad tooth, and many other serious reasons.
What we will cover in this article:

The reasons
Ear pain varies
There are many types of pain. They can be caused by various factors, such as infections of the respiratory tract, mouth, and other organs.
The type of pain also depends on where it occurs:
- The auricle, which is responsible for capturing sounds. In windy weather, be careful. Strong air currents can leave a bruise, which can later develop into a bluish hematoma. Also, pain can be caused by various temperature effects, such as hypothermia or burns. The auricle is very sensitive to such influences.
- There is such a disease as perichondritis. This is a skin disease on the cartilage. This cartilage is responsible for the shape of our nose and ears.
- External auditory meatus. When foreign objects enter the external auditory canal, pain occurs. In the future, it can turn into inflammation of the ear. Most often, this problem is faced by young children.
- When dirty water gets into the ears, severe inflammation can occur. Thus, the infection provokes acute inflammation of the external ear. Even the work of the jaw can aggravate the situation.
- Furunculosis. We all know that there is hair in the ears. So there are even inflammations of the hair follicles located in the ear canal. In this case, there are strong painful sensations. Even the movements of the jaw and ears complicate the situation. If you press the cartilage (tragus), which we have already talked about, you may feel unwell.
- Factors such as humidity, dampness and heat can cause swelling of the skin in the ear. If you spend a lot of time in the water, the skin in your ears becomes soft and, therefore, vulnerable. Such a background is favorable for the reproduction of bacteria. Such an infection can result in inflammation of the middle ear.
- The protective function is the formation of sulfur in the ears. This is a natural process that is sometimes accompanied by complications in some people. To solve this trouble, there are special drops. They soften the accumulated sulfur in the ear. True, they do not always help. In this case, medical intervention is required. The doctor gently removes all excess by washing. A large formation of sulfur causes pain and also affects hearing.
- But the lack of earwax entails diseases. There is itching in the ear. One of the reasons for its appearance is a fungus. In the ear canal, all conditions for the development of this disease can be met.
- Inflammation of the middle ear is an infection that occurs due to bacteria that prevent fluid from escaping. Thus, it is always in the ear.
- A typical disease for babies is acute inflammation of the middle ear. With this disease, relapses often occur. Children complain of pain, fever, often cry.
- Another childhood disease is secretory inflammation of the middle ear. With it, a large amount of viscous fluid is produced, which collects behind the eardrum. Symptoms are: pain, hearing loss.
- If you have allergic rhinitis or sinusitis, you may be suffering from ear pressure. Ear pressure occurs due to stagnation of air flow in the Eustachian tube.

Ear pain that does not affect hearing:
- Acute and subacute inflammation affecting the external auditory canal.
- Diseases associated with the area of the jaw joint.
- Abscess and mumps of the parotid secretion.
- Inflammation that occurs in people with congenital parotid cysts.
- With inflammation of the lymph node - parotid lymphadenitis.
There are diseases that can indicate false ear diseases:
- Pain caused by problems with.
- Ulcerative and purulent processes in the larynx, pharynx, mandible, palatine tonsils.
- Neuritis of the cranial nerves, such as the vagus and intermediate, glossopharyngeal and others.
- Also neuralgia of the second and third branches in the cervical nerve plexus.
Pain in the auricles and tragus can occur when:
- Skin diseases and erysipelas in the ear.
- Furuncle of the ear canal and otitis.
- Diseases such as perichondritis and chondroperichondritis, that is, a disease of cartilage.
Treatment
Otinum. The drug is analgesic and anti-inflammatory. It is applied topically in otology. A derivative of salicylic acid is choline salicylate. Thanks to the glycerol, which is part of the drug, softening and facilitating the removal of earwax occurs. The drug does not have a systemic effect when applied topically. It is used for external acute otitis media, as well as for acute otitis media, tympanitis and moderately acute otitis media. Also used when washing the external auditory canals, when removing sulfuric plugs.
This drug has contraindications for use. Not recommended for use in case of individual intolerance, gastric and intestinal ulcers, bronchial asthma. Adults with acute otitis media and tympanitis are usually prescribed 3-4 drops in the external auditory canal three or four times a day. The duration of the course of treatment varies from the course of the disease.
To soften the sulfur plug before removing it from the ear, three or four drops are prescribed into the external auditory canal twice a day for four days.

After the end of the procedure, the patient should be in a position with the ear up. A few minutes is enough.
In infants, the drug should be used only under medical supervision. Children and elderly patients are prescribed in the same dosage as adults.
Otipax. It comes in the form of ear drops. Otipax is a combination drug that is applied topically. It has a good analgesic and anti-inflammatory effect.
Local anesthetic lidocaine and phenazone give a strong anti-inflammatory effect. Due to phenazone, the effect of the second component is greatly enhanced. Pain in otitis media is quickly eliminated by a combination of lidocaine and phenazone. Approximately 5 minutes after instillation, pain from inflammation of the eardrum decreases. And after 15–30 minutes, pain is not felt at all.
When applied topically, the components that make up the drug cannot be determined modern methods studies of blood and other biological media of the body. The drug is used in the treatment of acute otitis media, influenza, otitis media.
There are also contraindications. Should not be used for damage to the eardrum caused by infections and trauma; hypersensitivity to the components that make up the drug.
The drug is prescribed for children, starting from infancy, adults and adolescents - drip four drops into the outer ear several times a day. Treat no more than ten days.

Folk remedies
Alternative methods of treating otitis media (inflammation of the ear):
- One of the effective recipes is the instillation of warm camphor oil into the inflamed ear.
- Baked in the oven. When the juice appears, remove the bulbs and squeeze out the juice. Still warm, pour into the ear.
- Try to extract juice from walnut. The resulting oil, two drops, drip into the ears.
- With purulent inflammation, a mixture of onion and oil can help. To do this, you need a swab soaked in gruel or juice. onion, as well as linen or butter, put in the ear.
- Almond oil can be used as a pain reliever. Just drip into your ear.

- Another way to get rid of pain. It is enough to take a couple of pieces of onions and wrap them well with cotton wool. Ready-made tampons are inserted into the ears, however, not deep. After a while, the pain should go away. In addition, the airways will be cleared.
- Many people know medicinal properties propolis. All that is needed is to make a propolis tincture with. Propolis tincture on alcohol mixed with honey. Take a few drops every day before bed. This will help get rid of the pain of purulent inflammation.
- Buy or prepare a 40% propolis tincture yourself, and keep it in your personal home first aid kit all the time. Mix one part of propolis tincture with four parts of olive or vegetable oil, mix until an emulsion is obtained Brown color with a pleasant smell. Before use, shake and wet two gauze swabs and plug them into the ears for an hour. In total, 10-12 procedures must be done in one day. If there is such a need, you can do everything again in two weeks.
- One of the most common methods is heating. If discomfort occurs in the ears, pain and other symptoms, warming is used. To do this, it is necessary to heat the water so that it is moderately warm, and not boiling water. Make a cotton swab, or use an ear stick, soaked in water, put it in your ear. Do not take out until the water has cooled down. Repeat the procedure at least five times, not forgetting about warm water. This is the key to this type of treatment. It is recommended to do several approaches per day. Don't be lazy and get rid of the pain.

Before, when there were no doctors, our great-grandmothers faced the problem of ear inflammation. Some recipes are still used today. Here are some of them.
- A tablespoon of salt dissolves in one liter of water. Then everything mixes well. Add camphor oil to a 100-gram jar of ammonia, about ten grams. Shake the resulting mixture and mix with brine. White flakes should appear in the resulting product. Close the resulting mixture tightly and shake until everything becomes homogeneous. This tool has a good shelf life, at least a year. For every occasion you need, you have your own tincture for earache.
- The following recipe for deafness and pain may seem a little strange. Roll a huge sheet of thick paper into a funnel. Insert the narrower edge into the patient's ear and set the paper on fire. An almost burnt-out funnel will have to be knocked out of the ear with a light blow of the hand. Do this ritual with the second ear. If you believe this healer's method, then deafness and pain should immediately disappear.
- Warm compress - very effective remedy in the treatment of otitis media. A compress is applied for otitis media around the ear area. The gauze is rolled up in three or four layers with the expectation that the area of the compress should be about 10x10 centimeters. In the center of our bandage, a hole is made for the auricle. Then the bandage is moistened with vodka or water and placed on the area of the body around the affected ear. Basically, the compress is moistened with water or vodka. A piece of oiled paper or cellophane, cotton wool is applied on top and the compress is fixed with a bandage, or a scarf, or a suitable cap. This compress is placed at night.
- Compresses with vodka and honey are considered very effective. Honey can be dissolved in vodka and soaked with gauze or bandage. You can also anoint a vodka-soaked compress with honey on top. Very effective and reliable remedy in the treatment of ear inflammation.

Ear pain in a child
With any strange and restless behavior of your baby, special attention should be paid. After all, a small child can not yet tell about his problem. To check, you need to knock on the tragus. In case of illness, this will certainly cause pain in the child.
Due to the peculiarities of the structure of the ears, in childhood we are most susceptible to various infectious diseases. As a result, small children are leaders in ear diseases. Statistics say that by the age of six, almost 100% of children suffered from these diseases.
Exodus this disease unpredictable. Therefore, it is strongly not recommended to self-medicate. And also do not delay treatment. At the first symptoms, it is necessary to resort to the services of a doctor.

Prevention
- It is not recommended to use ear sticks and other similar items. Because of the stick, the wax can be even deeper in the ear, and this threatens to accumulate more of it far inside.
- When visiting pools and other bodies of water, you should take care of the safety of your ears. There are special earplugs that keep water out of your ears. Ears must be dry. To do this, you can use a hair dryer. And your ears will be protected after taking water procedures.
- Under harmful working conditions, such as noise, everything must be foreseen. It is recommended that you protect your ears not only at work, but even at home.
- The nose must be cleared of any liquids, so they should be disposed of frequently without squeezing the nose.
- Make sure that foreign objects do not get into the ear canal.
- It is very important to visit a doctor if you have any hearing problems. Look closely at your child's behavior. If he listens to music or TV loudly, is inattentive in class, or you just notice that he has become hard of hearing, be sure to take action. Go to an appointment with a specialist who, having done some procedures, will determine what and how.
This is the most common reason for unscheduled pediatrician calls. Sometimes parents worry no less than the child himself, and appropriate advice from a doctor, even over the phone, greatly alleviates this condition. Causes of ear pain in adults are much more varied than in children and can be localized in the auricle, auditory canal, middle ear, and structures adjacent to the ear (radiating pain).
Otalgia (ear pain) - periodic pain attacks in the auricle, external auditory canal and in the depths of the ear against the background of a normal state of health and an intact hearing organ.
Pathophysiology of ear pain
Pain may result from a pathological process in the ear itself or may radiate from some nearby organ.
Pain resulting from an ear lesion may be the result of a difference in pressure between the middle ear and outside and/or local inflammation. Acute otitis media leads to inflammation of the eardrum, which is accompanied by pain (and leads to swelling of the eardrum).
Radiating pain can occur as a result of damage to areas innervated by cranial nerves responsible for sensitivity in the outer and middle ear (5,9 and 10 pairs). These organs include: nose, paranasal sinuses, nasopharynx, teeth, gums, temporomandibular joint, lower jaw, behind the ear salivary glands, tongue, palatine tonsils, pharynx, trachea and esophagus. Diseases of these organs also often lead to obstruction of the auditory tube, causing pain.
Causes of ear pain
The origin of otalgia is not entirely clear. Possible vascular dysfunction or the influence of viruses.
Often, unpleasant pain occurs with local cooling and in wet weather, which leads to dysfunction of the vasomotors. As a rule, with radiating pain in the ear, an otoneurological examination reveals irritation of the IX, X, V cranial nerves. The vagus nerve gives off a branch for the innervation of the external auditory canal, the glossopharyngeal nerve is involved in the formation of the tympanic plexus. Irritation of the pterygopalatine node can also cause ear pain. Thus, in addition to hypothermia, radiating pain in the ear can be associated with neurogenic manifestations with ulcerative and tumor lesions in the pharynx and larynx, with cervical lymphadenitis, paratonsillitis, with salivary gland stones, malocclusion, inflammation of the ethmoid and sphenoid sinuses, etc., which requires further investigation.
Frequent causes:
- infectious otitis media: bacterial / viral;
- infectious external otitis: bacterial/fungal/viral;
- purulent inflammation and boils of the external auditory canal and auricle;
- trauma (especially with cotton swabs) and foreign bodies (including earwax);
- throat diseases: tonsillitis / pharyngitis / tonsillitis.
Possible reasons:
- dysfunction of the temporomandibular joint;
- tooth abscess;
- impacted molar;
- trigeminal neuralgia;
- eczema/seborrheic dermatitis of the external auditory canal;
- nodular chondrodermatitis of the auricle.
Rare causes:
- mastoiditis;
- spondylosis of the cervical spine;
- cholesteatoma;
- malignant disease;
- barotrauma.
comparison table
Middle ear:
| Cause | Feelings that arise | Diagnostic approach |
|---|---|---|
| Acute obstruction of the auditory tube | Less pronounced discomfort. There is a bubbling, crackling or rustling sound with or without nasal congestion. BP is not hyperemic, but mobility is reduced. Unilateral conductive hearing loss | Clinical examination |
| barotrauma | Expressed pain. A sharp change in atmospheric pressure in history (flights, scuba diving). Often hemorrhage on or behind the BP surface | Clinical examination |
| mastoiditis | A recent history of acute otitis media. There may be suppuration, hyperemia | Clinical examination. CT is sometimes used to assess the extent and presence of complications |
| Suppurative otitis media (acute or chronic) | Severe pain, symptoms of intoxication are often noted. Bulging and hyperemia of the tympanic membrane. More common in children. Possible presence of discharge during perforation of the tympanic membrane | Clinical examination |
Outer ear:
| Cause | Feelings that arise | Diagnostic approach |
|---|---|---|
| Sulfur plug or foreign body | Visualized by otoscopy | Clinical examination |
| Local injury |
As a rule, a history of ear toileting Damage to the ear canal, visualized by otoscopy |
Clinical examination |
| Otitis externa (acute or chronic) | Itching and pain (mostly itching and some discomfort in chronic otitis externa). Often a history of swimming or frequent contact with water. Sometimes discharge with an unpleasant odor is determined. The external auditory canal is hyperemic, edematous; purulent discharge. Normal PSU | Clinical examination. CT scan of the temporal bones for suspected malignant otitis externa |
Causes of a non-otogenic nature:
| Cause | Feelings that arise | Diagnostic approach |
|---|---|---|
| Cancer (nasopharynx, palatine tonsils, base of tongue, larynx) | Constant discomfort. Often a history of long-term smoking and alcohol consumption. Sometimes there is an average exudative otitis media, cervical lymphadenitis. | MRI with gadolinium contrast. Biopsy of visible lesions |
| Infection (palatine tonsils, paratonsillar abscess) | Pain when swallowing. Visible hyperemia of the oropharynx. Bulging with an abscess | Clinical examination. Streptococcus cultures are sometimes sown |
| Neuralgia (trigeminal, pterygopalatine, glossopharyngeal and geniculate nerves) | Pain of a different nature: shooting, sharp, acute, pronounced | Clinical examination |
| TMJ dysfunction | The pain is aggravated by movement of the TMJ joint. | Clinical examination |
Conductive hearing loss occurs with many diseases of the middle and outer ear. Very often the otoscopic picture is normal. BP - tympanic membrane; TMJ - temporomandibular joint.
Ear pain resulting from a pathological process in the ear (involving the middle or outer ear) or as a result of damage to nearby organs.
In acute pain, the most common causes are middle ear infections and outer ear infections.
For chronic pain (>2-3 weeks), the most common causes are
- TMJ dysfunction,
- chronic infection of the auditory tube,
- chronic otitis externa.
Also, in the presence of persistent pain, it is necessary to exclude the oncological process, especially in elderly patients and if the pain is accompanied by otorrhea. It should be noted that patients with diabetes or other immunocompromised patients may develop severe otitis externa, often with a malignant necrotizing course. In this case, if pathological soft tissues are found in the external auditory canal, a biopsy should be performed to rule out cancer.
Dysfunction of the TMJ joint is a common cause of otalgia in patients with normal otoscopy.
Ear pain test
Painful sensations in the ear often baffle the outpatient doctor, who does not detect a pathological substrate in the ear during otoscopy and normal functional examination. Tactile irritation (with a cotton swab, a button probe) of the skin of the external auditory canal and auricle, as well as the skin of the face and the mucous membrane of the pharynx on the corresponding side reveals either hypesthesia (weakening of sensitivity) or hyperesthesia (increased sensitivity) compared to the opposite side.
Examination methods
Main: none.
Additional: ear swab.
Auxiliary: radiography of the temporomandibular joint, teeth and mastoid process, OAK, Paul-Bunnel reaction.
An external auditory canal swab is useful if there is discharge after unsuccessful first-line empiric therapy.
X-ray of the mastoid process helps to exclude mastoiditis, usually performed by a specialist. X-rays of the temporomandibular joint and teeth are performed by dentists or maxillofacial surgeons.
OAK and the Paul-Bunnel reaction should be performed if infectious mononucleosis is suspected. The diagnosis provides direction and further recommendations, although there is no specific treatment.
Further special studies may include CT/MRI as the only way to adequately (non-invasively) examine the anatomy of the inner ear and temporal bone.
The presence of foreign bodies in the ear canal will prevent resolution of otitis externa and mask possible reasons underlying. Hearing hygiene is extremely important.
If pain appears during examination with an ear mirror, it is most likely associated with otitis externa or a boil.
Be sure to ask about the injury, especially if the patient uses cotton swabs. Extraction of earwax with sticks often leads to inflammation of the external auditory canal and eardrum, mimicking an infectious process.
Ear pain can be excruciating, so don't underestimate the role of adequate pain relief while you're identifying and treating the cause.
If there is foul-smelling discharge from the ear for more than 10 days, mastoiditis should be suspected. Check for swelling behind the auricle and its downward displacement.
Do not rush to diagnose otitis media in children: diseases of the upper respiratory tract and crying inevitably lead to varying degrees of redness of the eardrum. Indiscriminate drug prescribing can lead to iatrogenic problems and mask the true cause.
Be alert to elderly patients with unresolved and unexplained ear pain: Nasopharyngeal carcinoma must be ruled out.
Anamnesis. When studying the anamnesis of the present disease, it is necessary to pay attention to the localization, duration and severity of the pain syndrome, as well as to clarify whether the pain is permanent. If the pain is intermittent, then it is necessary to clarify whether it occurs suddenly or during swallowing or jaw movement. Important symptoms also include the presence of discharge from the ear, hearing loss and sore throat. It is necessary to clarify with the patient whether there have been attempts to toilet the external auditory canal (for example, using cotton swabs), whether there have been foreign bodies in the external auditory canal, flights or scuba diving, swimming, or frequent contact with water.
In the study of organ systems, it is necessary to find out about the presence of chronic diseases, such as sudden weight loss and inflammatory diseases.
It is necessary to clarify the presence of other diseases in the anamnesis, such as diabetes or other immunocompromising conditions, previous ear diseases (especially infections), and the amount and duration of tobacco and alcohol use.
Instrumental inspection. At high temperatures, it is first necessary to examine vital functions.
The examination should focus on examining the ears, nose, and oropharynx.
It is necessary to carefully examine the auricle and the area near the mastoid process for hyperemia and swelling. The tympanic membrane is examined for hyperemia, perforations, and signs of fluid in the middle ear (bulging or deformity of the AP, changes in the light reflex). Perform a simple hearing test at the bedside
It is necessary to conduct pharyngoscopy for hyperemia or redness of the mucosa, swelling of the palatine arches, asymmetry of the pharynx and mucosal lesions, which may indicate cancer.
The neck should be palpated to rule out lymphadenopathy. It is possible to conduct an additional fibroendoscopic examination of the pharynx and larynx, especially in cases where no causes of pain have been identified during routine examination. In the presence of non-otologic symptoms such as hoarseness, difficulty swallowing, or nasal congestion, fibroendoscopy is also recommended for a detailed examination.
Key facts. Particular attention should be paid to the following clinical examination data:
- Diabetes or immunocompromising diseases.
- Redness and fluctuation in the projection of the mastoid process, as well as protrusion of the auricle.
- Severe swelling in the external auditory canal.
- Chronic pain, especially if other head/neck symptoms are present.
Interpretation of symptoms. A normal otoscopic picture is an important factor in the differential diagnosis; the otoscopic picture always reflects the pathology of the middle and outer ear and often indicates possible causes of the disease. For example, in patients with chronic eustachian tube dysfunction, PD pathology is always detected, usually in the form of retraction pockets.
In patients with a normal otoscopic picture, ear pain may be radiating in the pathology of the oropharynx: acute tonsillitis or paratonsillar abscess. Ear pain as a result of neuralgia has a classic presentation in the form of short episodes of sharp pain. Pain of a chronic nature with a normal otoscopic picture is more likely to occur in the pathology of the TMJ joint, and it is necessary to carefully examine patients (including fibroscopy) to exclude oncology.
Survey. In most cases, the diagnosis can be made after a thorough history taking and clinical examination. However, depending on the findings of the clinical examination, additional testing may be required to identify non-otologic causes of pain. Patients with a normal otoscopic appearance, especially those with persistent or recurrent pain, may need an MRI to rule out cancer.
Ear pain treatment
Treatment is conservative (analgesics: nurofen, pentalgin, etc., thermal procedures: heating pad, compress).
It is necessary to treat the underlying disease.
For relief of pain, as a rule, oral forms of NSAIDs are used, acetaminophen has a good analgesic effect. However, with severe pain, especially with aggressive otitis externa, the use of oral opioid drugs in a short course is recommended. In some cases, for effective treatment otitis externa, it is necessary to conduct a toilet of the external auditory canal (removal of epidermal masses) and the introduction of turunda with an antibacterial drug for better delivery of the drug. Topical analgesics (eg, antipyrine benzocaine) usually have a limited duration of action.
It is necessary to warn the patient that he should not independently toilet the external auditory canal using foreign objects (even using very soft objects and no matter how carefully the patient does this). Also, patients should not independently wash the ear canal. If the doctor has recommended flushing, then you should perform them with caution.
There is hardly a person who has not had earaches at least once in his life. Ear pain can be different: dull, pulling, throbbing, piercing. Often it is accompanied by laying the ears. If the ear hurts, we are talking about the presence of problems in the external ear canal, middle ear or eardrum.
There are many reasons for the development of pain, the most common of which are infection, irritation, pimples, blockage with earwax. After swimming, there is also a possibility of inflammation of the ear canal. Regardless of the cause of the pain, without fail remedial action should be taken immediately. The risks of developing complications with such symptoms are quite high.
Causes of ear pain
Causes of ear pain: most often the cause of pain is some kind of organic disease. The ear is extremely sensitive, so pain can occur even with slight inflammation. Inflammation of the external ear canal (otitis externa) or inflammation of the perichondrium (perichonditis) are very painful. Other common causes of ear pain are listed below.
Inflammation of the middle ear
Inflammation of the middle ear (otitis media) occurs as a result of penetration of infectious agents from the nasopharynx through the auditory tubes. Diseases such as adenoids and polyps play an important role in the occurrence of otitis media. As a result of the penetration of viruses into the middle ear, inflammation of the tympanic cavity develops, pus forms. Inflammation of the middle ear is accompanied by severe pain. Possible perforation of the eardrum and suppuration from the ear. Otitis media is especially common in young children. Apparently, the auditory tubes during this period are still short and wide, so the infection easily enters the middle ear cavity. Inflammation of the middle ear requires treatment, otherwise, inflammatory process may spread to bone.
Catarrh of the Eustachian tubes
Adenoids, edema as a result allergic reaction or inflammation of the nasopharynx can cause blockage, a feeling of congestion in the ears. Typically, these symptoms occur with hypothermia. Due to the change in pressure, the eardrum is pulled inward, causing pain. Inflammation of the external auditory canal (otitis externa): inflammation of the external auditory canal (lat. otitis externa) can also cause pain. There are two forms: limited - furuncle of the external auditory canal and diffuse. Localized otitis externa occurs as a result of infection in the hair follicles (folliculitis). With diffuse otitis externa, inflammation covers the entire auditory opening. The patient feels especially severe pain when pressing on the auricle.
Sulfur plugs
Sometimes pain in the ear, a feeling of congestion occurs with excessive accumulation of sulfur in the external auditory canal. Usually the reason for the accumulation of wax in the ears is their improper cleaning (the corner of a handkerchief, sticks with cotton swabs). Sulfur plugs are removed by an otolaryngologist.
Tumors
Ear pain can be caused by a tumor in the external auditory canal. The tumor can completely close the ear canal and prevent the release of wax from the ear, which impairs hearing. Ear tumors are removed surgically.
Other reasons
Ear pain may be the first symptom of diseases of the nasopharynx and paranasal sinuses, throat, may occur with various diseases temporomandibular joints, lower jaw, diseases of the teeth and gums. Ear pain may be the first sign of a tumor in one of these places. Ear pain can be caused by trauma or a foreign body that has entered the ear canal.
Ear pain treatment
In case of pain in the auricle and external auditory canal, it is necessary to avoid water ingress and unnecessary trauma to the skin when cleaning the ear. You can enter a shallow turunda with celestoderm ointment, lorinden, triderm. It is advisable to take painkillers in tablets (ketanov). Even if the symptoms subside, this does not eliminate the need to go to the doctor. Any purulent processes are dangerous and require control. If the pain in the ear is “shooting”, the body temperature rises to 38.00, it is necessary to create heat in the ear. This is achieved by introducing a turunda with boric alcohol into the ear canal or by applying an alcohol compress to the auricle. In such cases, painkillers are required.
Since otitis media is often complicated by paresis of the facial nerve, it is imperative to see a doctor. Otitis media in children can cause severe complications. If there is discharge in case of pain in the ear, then do not bury anything into it, do not inject turundas (only with saline), avoid water and immediately consult a doctor - most likely there is a perforation of the eardrum. Even worse, if the temperature is above 38.00, and nothing flows out of the ear - do not warm (just keep your ear warm), consult a doctor - this can be a closed purulent inflammation without an outflow of pus, often happens in children, especially small ones. Severe ear pain can be a symptom of labyrinthitis.
It is important to distinguish which disease you are facing. With severe acute pain in the ear, you need to establish its cause and do not immediately fill the ear with a variety of drops. With external otitis, putting compresses on the ear and introducing turundas with an alcohol solution into the ear canal is contraindicated - the pain will only increase due to the irritating effect of alcohol. With otitis media, instillation of antibiotics into the ear does not help much. If the tympanic membrane has broken through and the ear is “leaking”, it makes sense to introduce a turunda moistened with ordinary saline and change it every 2-3 hours on the way to the doctor. Burying anything with perforation of the eardrum, especially containing salicylates, is dangerous - you can damage the structures of the inner ear.
Child's ear hurts
Ear pain in children, usually severe, is one of the most common causes visits to the doctor or calling an ambulance even at night. Older children themselves can indicate the place of pain. The cause of pain in younger children is established during examination, sometimes by the release of fluid from the ear canal. Small children simply cry loudly or rub their sore ears. Sometimes ear pain is combined with a runny nose, an increase in cervical lymph nodes, tonsillitis, and a rise in body temperature above 38 ° C.
Causes of ear pain in children
- inflammation of the middle ear;
- inflammation of the ear canal;
- foreign body;
- abscesses in the ear;
- trauma;
- teething;
- tonsillitis;
- mumps (mumps);
- sulfur plug.
First aid for ear pain in a child
Every parent should know how to act while waiting for an ambulance to arrive when a child has an earache. This knowledge will help to cope with panic and relieve the unbearable pain in the baby's ears, which makes him act up. First of all, you need to give the child any painkiller that can be taken at his age and can relieve pain.
If there is a temperature, you can give an antipyretic medicine, as well as give the crumbs to drink as much water as possible. We must try to calm the child: shake in his arms, tell a story, sing a song. In the absence of temperature, a foreign object, a warming compress can be applied to the ears, after lubricating the ear and the skin around it with baby cream:
- First layer: gauze soaked in a vodka solution (water + vodka in equal proportions), folded into five layers. It must be wrapped around the ear, making sure that the auricle remains free.
- Second layer: cellophane or parchment paper, completely covering the gauze (it is necessary to cut it in half, push the auricle through the cut).
- Third layer: put a very thick piece of cotton wool.
- Fourth layer: secure with a bandage, bandage or warm scarf.
Keep the compress on the ears for about an hour, then remove. If there is no vodka at home, you can simply insulate the ear by attaching a large piece of cotton wool to it and fixing it with a bandage. Such a bandage will create a thermal effect in the ears, which will reduce pain. It should be borne in mind that it is strictly forbidden to make a compress in the presence of temperature, as well as pus from the ears.
Questions and answers on the topic "Pain in the ear"
Question:Hello. Recently, my ear often hurts. Even when there is no exacerbation, I press on the tragus and feel a little pain. Doctors say that there is no crime, but, apparently, a nerve is caught. It must be assumed that in the future it will hurt even more often. Is there any way to radically cure this stiffened nerve or is it for life?
Answer: Hello. With neuralgia of various origins good effect give physiotherapy (UHF, magnetotherapy), laser therapy. In addition to consulting an ENT doctor, an examination by a neuropathologist and a dentist is necessary to rule out other causes that can cause radiating pain in the ear (diseases of the teeth, lower jaw joint, pathology of the cervical spine).
Question:Hello. The child's ear hurts for the fourth day. At first I thought he was feigning, he did not want to go to school, but for the fourth day he complains of pain in his ear. Tell me what it could be Should I wait for it to pass or should I go to the doctor tomorrow?
Answer: Hello. Causes of ear pain can be: infection middle ear (otitis media); inflammation of the external auditory canal (otitis externa); foreign object getting into the ear; boil; trauma; tonsillitis; epidemic parotitis (mumps). In any case, it is necessary to consult a doctor to establish a diagnosis and prescribe the correct treatment.
Question:Hello. I decided to clean my ears by washing in the shower and then holding a cotton swab, now my ear hurts. What to do? I tried to rinse - first with hydrogen peroxide, then with water - did it help to contact an ENT doctor?
Answer: Hello. You need to go to an ENT doctor to examine you. Perhaps the eardrum has been punctured. can not be washed, because. if the eardrum is damaged, this is strictly prohibited (and even most types of ear drops can only be instilled if you are sure that the eardrum is intact). You need to see a doctor as soon as possible.
Question:Hello! I have had pain in my left ear for 2 years. As soon as it started to hurt, I went to the doctor and they said that it was otitis media. Then the otitis went away. The ear still hurts at times, but the doctors say that everything is fine! But it hurts me! What do you think it could be then?
Answer: Hello. If you have flown in an airplane, you have probably experienced pain in your ears while climbing. So in a person, they hurt because of swelling of the auditory tube connecting the ear to the nasopharynx (if it is not otitis externa). Causes (adenoids, runny nose, sinusitis, pharyngitis, deviated nasal septum). The task is to unblock the auditory tube (vasoconstrictor drops such as nazivin, galazolin, rinofluimucil; nasal antiseptics such as miramistin; decongestants or anti-inflammatory drugs such as claritin, erespal, you can also nurofen). You can flixonase (nasonex, nasobek) in the nose 2 times a day for a month. Rule out sinusitis (sinus x-ray) and fluid in the ear (tympanometry). Chew gum. Blow air through your ears by covering your nose and mouth with your fingers. And there is no point in dripping drops into the ear, the medicine does not penetrate through the eardrum.
Question:Hello! Why do children vomit when they have earache?
Answer:
Question:Hello! I have chronic tonsillitis, I periodically go to Laura. Now the condition of the tonsils is good. But 2 weeks ago, my ears got sick, and on both sides at the same time. Lor looked - she said neuralgia, because the membranes are good. I used my own solution to drip otipax for 2 days, and the pain went away. 3-4 days ago I was on a business trip, I froze. Sore throat, and more on the right side, and the right ear was very sore. Laura visited, she said - pharyngitis, prescribed treatment, but about the ear again - neuralgia, no need to treat. And I can not live without treatment - it constantly whines and sometimes twitches, it hurts a lot. Moreover, it hurts as if from the place where the throat is, it intensifies when swallowing. Please advise something. Go back to Laura? Or a neurologist?
Answer: Hello. Otitis is an insidious disease, depending on random circumstances, such as, for example, individual characteristics structure of the middle ear and concomitant diseases of the ENT organs, it can be severe, spreading to the deep parts of the hearing organ, the eardrum and the vestibular apparatus (organ of body balance). It is inflammation in the region of the vestibular apparatus that causes dizziness and vomiting. From your words it follows that the inflammatory process has gone far and "deep". I suppose that the child cannot be cured with home remedies, it is necessary to show the ENT doctor, who will determine the tactics of treatment.
Perhaps, any adult is familiar with aching pain in the ears. It is as unbearable as the toothache. The presence of pain can signal a serious illness, so their initial manifestations should not be underestimated. Any pain indicates changes in the body, that a certain system of it requires attention. When the ear hurts, it often indicates an inflammatory process.
To establish a diagnosis, timely treatment, and prevent serious complications, you need to undergo a medical examination. The danger of a situation when the ear hurts lies in the fact that, without due attention, this can lead to unpleasant consequences and even cause disability due to the loss of the ability to hear.
Otitis - the main cause of ear pain
Acute pain in the ear is one of the symptoms of a common disease - otitis media. The occurrence of the disease is provoked by viruses: pneumococcus, streptococcus, staphylococcus. Prerequisites for otitis are the following reasons:
- Penetration of infection in various ENT diseases. With a cold, mucus enters the Eustachian tube, blocking it. The pressure changes, inflammation forms, pain in the ear appears;
- Injuries to the outer part of the ear;
- Diseases of the nose. These include rhinitis or a deviated septum;
- Hypothermia, reduced immunity.
Main symptoms:
- Earache;
- The ear opening itches and itches;
- Ear congestion, feeling as if water had run out;
- Otitis media is often accompanied elevated temperature.
 Otitis is different depending on the location of the inflammation. Otitis externa is usually associated with microtrauma,. In acute external otitis, the patient experiences pain in the ears due to the appearance of boils and purulent abscesses on the walls of the auricle. Symptoms of the inflammatory process are common for otitis media: fever, ear congestion. The auricle is very itchy.
Otitis is different depending on the location of the inflammation. Otitis externa is usually associated with microtrauma,. In acute external otitis, the patient experiences pain in the ears due to the appearance of boils and purulent abscesses on the walls of the auricle. Symptoms of the inflammatory process are common for otitis media: fever, ear congestion. The auricle is very itchy.
If the patient experiences a sharp, bursting pain in the depths of the ear, then this is a manifestation of acute otitis media.
The disease is localized in the region of the middle ear, that is, behind the eardrum. The children's form of the disease is accompanied by a runny nose, and the ear also hurts and the body temperature is elevated. With a purulent tympanic membrane often breaks through, the pain in the ears gradually disappears. Otitis requires a mandatory examination by a doctor for appropriate treatment. The otolaryngologist diagnoses the broken integrity of the eardrum, prescribes the appropriate medications. When the patient is often dizzy. Inflammation occurs in the region of the inner ear, which is responsible for spatial orientation.
Features of otitis media in childhood
Children quite often suffer from acute purulent or. The child's ear is not fully formed. The Eustachian tube in children is wider, shorter, it is located almost horizontally, which facilitates the penetration of infection from the nose into the ears. Children's immunity is very weak. A small breeze in the child's ear after a warm bath is enough, a runny nose immediately appears, which, with irrational treatment, easily provokes otitis media. Age features of childhood otitis media:
- In infants with otitis media, the process of breast sucking causes strong “shots” in the ear. The baby cannot name the cause of the anxiety. In such situations, the attentive attitude of the mother to the behavior of the child helps a lot to identify the disease. If during the day the behavior of the baby does not yet cause concern, then by the evening the pain intensifies. When feeding, the baby literally arches in an “arc”, begins to cry a lot.
- Older children already clearly explain that their ears hurt. Ear pain is accompanied by fever, chills, refusal to eat (when chewing, swallowing Blunt pain increases), gastrointestinal disturbances, vomiting, diarrhea are observed. In the end, the pain becomes unbearable, the baby is hysterical. The deterioration of the child's condition usually occurs in the evening, do not wait for the morning. An ambulance should be called - the child will still not fall asleep from pain. Before the doctor arrives, it is advisable to give painkillers by putting the child to bed.
To treat and get rid of phlegm, our readers successfully use a natural remedy for phlegm. This is a 100% natural remedy, which is based exclusively on herbs, and mixed in such a way as to most effectively fight the disease. The product will help to quickly and effectively defeat cough in short time and once and for all. Since the drug consists only of herbs, it does not have any side effects. Does not affect blood pressure and heart rate. Get rid of mucus ... "
Perichondritis and mastoiditis as a cause of pain
Perichondritis is an infectious disease. The cause of swelling of the auricle is Pseudomonas aeruginosa, less often other bacteria act as a source of the disease.
A sign of the disease is swelling, redness of the auricle, pain and inflammatory symptoms are mild.
Perichondritis is provoked by the following reasons:
- Traumatic damage to the auricle, a simple scratch can cause illness. Violation of the integument of the external auricle becomes the impetus for external infection. The presence of a pathogenic pathogen infection inside the body also provokes the disease. This also includes burns, frostbite, and other injuries;
- Furuncle on the auricle;
- Complications after influenza, tuberculosis, consequences of piercing (infection during puncture), surgery. Perichondritis may develop as a consequence.
The purulent form of perichondritis is characterized by an increase in temperature, the ear becomes softened, cyanotic, bumpy, filled with pus. On palpation, the patient experiences severe pain. Due to purulent softening, the ear deforms over time, cartilage tissue dies off. Mastoiditis can spread to the left or right ear. Behind the ear is the mastoid cavity. It can become inflamed, causing pain in the ear. This is an infectious inflammatory lesion of the mastoid process of the temporal bone. The disease is one of the complications after suffering otitis media. The disease is diagnosed by the following signs:
- The ear hurts and the temperature rises to 38-39 degrees;
- Sharp headache;
- General intoxication of the body, weakness, lethargy, drowsiness of the patient;
- Inflammation, swelling behind the ear of the head;
- Hearing is greatly reduced.
If you have symptoms of the disease, you should immediately seek medical help from a doctor. Mastoiditis is atypical, typical, children's. Typical is characterized by severe redness, pain when touching the ear. For atypical form The disease is characterized by a pulling pain near the ear.
Diseases that cause earache
Lymphadenitis - can be the cause of a condition when a person has an earache.  This disease is an increase in the lymph nodes that are located outside the auricle. There is pain in the ear, which is accompanied by migraine, fever. Wax buildup also often causes ear pain. It penetrates deep into the ear canal and begins to put pressure on the membrane. There are a number of diseases that are not associated with the inflammatory process in the ear. However, they cause pain, causing significant discomfort.
This disease is an increase in the lymph nodes that are located outside the auricle. There is pain in the ear, which is accompanied by migraine, fever. Wax buildup also often causes ear pain. It penetrates deep into the ear canal and begins to put pressure on the membrane. There are a number of diseases that are not associated with the inflammatory process in the ear. However, they cause pain, causing significant discomfort.
These diseases include:
- Diseases of the teeth;
- Neuritis, neuralgia;
- Ulcer, inflammation of the larynx, jaw, tonsils.
Ear pain due to mechanical damage
Ear pain in an adult is usually associated with the following injuries:
- or barotrauma. Occupational illness of divers and pilots, arising from a strong air pressure drop: external and inside the ear. Ears can be severely injured and have ordinary people during an unprofessional sudden dive or takeoff of an aircraft;
- Foreign object inside the ear. The entry of objects into the ear canal is one of the most common causes of ear pain. Often this happens to children, during the game they can accidentally push small objects into their ears. Adults usually get such an injury when they get into the auricle of an insect. It is important to know that if a foreign object gets into the auricle, you should not try to pull it out yourself. Since inaccurate, inept actions can cause injury. The ear can hurt from hypothermia or various injuries. The ear of an adult is periodically damaged by careless handling of cotton swabs. Mechanical damage to the eardrum is often irreversible.
- Furunculosis is a disease when the ear also hurts. This disease is associated with an infection in the hair follicles located on the surface of the ear canal. Ears "shoot through" when a person moved his jaw or simply touched his ear.
The cause of ear pain that does not lead to hearing loss can be:
- Acute, subacute inflammatory process occurring outside the auditory canal. In this case, there is no complete blockage of the auditory canal;
- Arthritis, arthrosis, spreading to the jaw joint;
- Various mumps, abscesses involved in the parotid gland;
- A disease associated with inflammation of congenital cysts located near the ear;
- Inflamed lymph nodes under the jaw, next to the ear.
Thus, ear pain is a sure sign of some kind of inflammation in the body. It can be bright and pulsating or monotonous and pulling. Earaches often appear as a result of otitis media. But there are still a number of diseases that provoke or mimic ear pain. Careful attention to your own body and appropriate treatment always helps to avoid complications.
