If you are engaged in manufacturing activities or are engaged in speculative resale of certain product items, cost of sales is the most significant parameter for you. To calculate this value, it is necessary to have some other indicators. The subtleties of calculation actions and basic rules will be discussed within the framework of this material.
Cost is the totality of costs (expenses) that went into the production process of a product. Traditionally, this includes costs related to units produced. But such a variant of calculations is also possible, within the framework of which administrative and commercial expenses are allocated to the cost of the final product.
This is one of the basic parameters related to accounting reporting, coming directly after sales revenue. If you subtract the cost of sales parameter from revenue, you get gross profit, which can be positive or negative. As for other general business expenses, they also act as part of the financial result. This is not all that is included in the cost of sales, since this indicator is very extensive and generalized.
Cost of sales: varieties and classification
The cost of sales parameter can be considered in the context of cost areas and costing elements. There are several key cost elements:
- material part (this includes raw materials, materials, components, general production costs);
- personnel costs;
- deductions from salary - insurance, pension payments and other items;
- costs associated with depreciation (depreciation) of fixed assets.
Calculation of current expenses
There is also a classification by article, which depends on the industry characteristics of the company. Traditionally, in practice there are several fundamental expense items:
- raw materials and materials;
- returnable waste;
- purchased components;
- fuel and energy resources;
- labor costs;
- contributions for social needs;
- production development costs;
- losses associated with marriage;
- sales costs.
When considering the question of what cost of sales is, it is worth considering two more classification criteria. It can be average or extreme. As part of the full indicator, it implies the volume of all waste associated with production activities, including commercial expenses. As for the marginal cost, it is represented by the price of a unit of product that is produced.
Within the framework of practice, there are several key types of cost.
- Shop. It assumes the total value of all consumables that were incurred by all structures influencing the process of creating a product.
- Production. Within its framework, the organization's expenses are recorded. You can also talk about general and target costs here.
- Full. This indicator assumes that the main expenses include the money spent on the final process of selling the product. That is, logistics-related costs are added here.
There are several other terms that define the cost indicator.
Conducting a cost analysis
Cost serves as the most important indicator for analysis aimed at improving production efficiency. It can be implemented in several directions. For example, all expenses could be:
- variables(depending on the volume of output) - costs of warehousing and storage, purchase of raw materials, payment of wages to employees;
- permanent costs (independent of the quantity of products produced) - advertising costs, costs of renting premises, salaries of management personnel.

Types of costs (expenses) on the chart
Thanks to the implementation of this type of analysis, it is possible to determine the production volumes within which the enterprise can recoup its costs, that is, reach the break-even point and begin to make a profit. The source for analytical activities is accounting, as well as warehouse and production data. It is possible to carry out a cost analysis based on public reporting information only in a general way, determining only the trend of costs and profits (growth or decline). To ensure the implementation of more in-depth analytical activities, it is necessary to use data located in the enterprise accounting system.
How to carry out settlement activities
The cost of goods sold has certain calculation methods. To determine this indicator, you must have information about other company data.
- The price of inventory on hand at the beginning of the year. If this indicator differs from the price of inventory items at the end of the last annual period, it is worth finding an explanation for this phenomenon.
- The probable cost of purchases, assuming the exclusion of goods that were taken for personal use.
- Cost areas that were used to pay employees. From these it is necessary to exclude amounts that are allocated for yourself.
- Cost of materials and other supply elements.

Analytical cost accounting
After determining all these parameters and elements, you can answer the simple question of how to calculate the cost of sales and do it as rationally as possible. After all, these indicators are the most important, and they must be present as part of your reporting documents. To carry out calculation actions, it is necessary to add up all these parameters. To do this, it is enough to subtract the sum of other indicators from the amount of inventory, and it will not be difficult for you to determine the cost of selling products.
The most common calculation methods
Traditionally, a publicly available formula is generated in accordance with the full volume of expenses taken into account. There are several options for action - a regulatory option, by order, by process. Each of them has a basis in the form of a classic version of determining the full cost. In order to obtain the parameter for the total cost of manufactured units of production, it is necessary to sum up all the values of workshop and other rasters. Shop cost of sales consists of several components:
- operation of equipment along with its practical application;
- expenses for electricity and the purchase of process fuel used as part of the production process;
- payment arrangements for obligations, wages for key workers;
- a complete list of shop expenses, including depreciation, inventory, and various deductions.
Special attention is paid to the company's general production costs, which include salaries of management personnel, travel expenses, and costs of maintaining guards. In this regard, calculation actions are performed in a certain sequence.
- Identification of variable costs associated with the creation of one product unit, taking into account costly activities.
- Determination of types and directions of expenses directly related to the type of products produced.
- Carrying out the summation of related expense transactions that are not related to production-type costs.

Current costs of the company
If the total cost of production is increased, the cost of its sales will increase. And this will negatively affect the competitiveness of the product in the market and the company’s ratings.
General view of the formula
The method by which costs will be calculated depends on the degree of readiness of the product units. The generalized type of formula is as follows.
- Production costs:
Cost = Material expenses + Depreciation deductions + Payroll expenses + General expenses. - The generalized type of formula for calculating the total cost has the following appearance, which is important to take into account.
PS = production costs + non-production costs. - Calculation of the cost of a product that has been sold is carried out according to the following principle:
SP = PS + commercial expenses - the remains of products that were not sold. - Production costs can be calculated based on the following formula.
PS = cost of gross product - changes that have taken place in the balances of work in progress. - The cost associated with gross output is equal to the following value:
BC = Production costs - non-production areas - future expenses.
So, we looked at what areas cost of sales includes. To have an idea of the company’s activities as a whole, it is necessary to competently carry out analysis and calculate the main parameters. This will allow you to always be aware of the need to take measures that are necessary to improve commercial activities and improve the main economic indicators of commercial activity.
The production of any type of product is inevitably associated with costs: raw materials, electricity, transportation, workers' compensation, transfer of taxes to the budget, and others. It is advisable to reduce them; It is impossible to do without them completely. And in order to determine how much money the company needs to reimburse at the end of the product production cycle, you need to calculate the cost using a simple formula. It is also necessary to determine production as a whole.
The cost per unit of goods, like , can be calculated either manually or in the Microsoft Excel application designed for working with spreadsheets. The latter option is preferable: once creating a template or using a ready-made one, the user can subsequently make calculations simply by substituting new data into the example. We’ll talk about how to calculate the cost per unit of production in Excel.
Calculation of unit cost in Excel
SS= ΣР / О, where
- SS- cost;
- ΣР- the sum of all expenses incurred by the manufacturer;
- ABOUT- the total quantity of products produced in natural units (kilograms, meters, liters, pieces, and so on).
In the future, using the obtained value, you can calculate the market price of products, income and carry out other necessary actions. This can be done both in MS Excel and in specialized programs.
Important: the composition of expenses taken into account in the calculation of product costs should be determined taking into account the characteristics of production. There is no general list of articles, as with . For example, to make plastic photo frames you will need to purchase special glue, and to produce ball bearings you will need grinding materials and lubricants. In the first case, they are not needed, nor are adhesives in the second.
Unlike, which is quite difficult for an untrained user, even a beginner can calculate the cost of production in production in an Excel spreadsheet. Below is a small example of working with a spreadsheet.
A simplified procedure for calculating the cost of a product:
- In the first column of the e-book (it can be located anywhere on the page; the concept of “first” in this case is purely conditional) under the name “Product” you need to enter the name of one or more types of products.

- In the second column (“Raw Materials”) - the cost of raw materials or consumables purchased for the production of each specific type of product in rubles or any other applicable currency. If necessary, you can list the costs for each type of raw material used, and then calculate the amount: for example, to produce a plastic nesting doll, you will need to separately purchase plastic or hydrocarbons, paint, and decorative metal elements. However, in most cases, in order not to overload the table, to determine the cost of production it is enough to indicate the total amount without exchanging details.

- In the third column (“Transport”) - the costs of transporting raw materials (also in rubles or other local currency).

- In the fourth column (“Energy”) - the enterprise’s costs for providing the production line with electricity (also in rubles).

- In the fifth column (“Defects”) - the average percentage of defective products and waste for one production cycle (in percentages or shares).
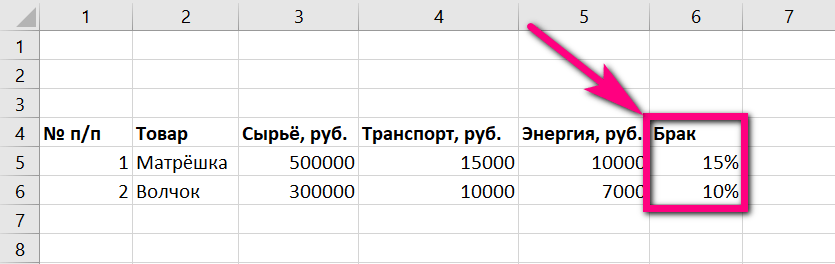
- In the sixth column (“Salary”) - the total wages of employees employed in production.

- In the seventh column (“Quantity”) - the quantity of each type of product produced (in kilograms, liters, pieces, and so on).

- In the eighth column (“Amount”) you need to sum up the previously entered data.
- In order to calculate the sum, you should single-click the appropriate cell, press the “=” key and, successively clicking on the cells that make up the formula, sum, multiply and divide the values. To finish the calculation, you just need to use the Enter key. The result in rubles will be displayed in the same cell in which the calculations were made.

Advice: To check the correctness of the formula used, there is no need to double-click on the cells of the “Amount” column each time. You can simply mark the desired item with a single click: the order of arithmetic operations will be displayed in the top “status bar” of MS Excel.

The results obtained can be copied to a reporting form or, as in the case with, continue calculations in a spreadsheet editor.
Calculate production costs - download Excel template and sample
You can download a template for calculating the cost of a unit of production in production in the form of an Excel document from the link above.
You can download a ready-made example, which allows you to understand in more detail the order of operations performed, from the link above.
Let's sum it up
The cost per unit of finished products can be calculated not only in specialized programs, but also in the Microsoft Excel spreadsheet editor. The data is entered into the table in the appropriate columns and then summarized. At the end, you need to divide the gross cost of the product by the number of natural units, expressed in kilograms, pieces, liters, and so on.
The user can create a template for calculations independently or download a blank form and a sample calculation from the links above. You can work with both the template and the finished example in Excel or any suitable editor. To see what formula was used in the calculation, just click once on the cell of interest and pay attention to the “status bar” located at the top.
The basis of any business is the process of control; you can talk a lot about desire, the ability to organize and the availability of start-up capital, but all of them become secondary without the ability to control. Why is this happening?
In fact, any models (mechanisms) built by humans require systematic “adjustment” because nothing is eternal on this planet, and when it comes to models built using people themselves, the problem is aggravated many times over. Alas, no one has canceled the “human factor”; any business is, first of all, a model of interaction between different people to achieve certain goals, most often making a profit. But the question arises of how you can monitor the functioning process itself and, of course, check how effective the work of the constructed model is. In fact, it was precisely for monitoring business processes, which is impossible without analysis, that such indicators as cost, . Moreover, with the development of economic relations, more “advanced” ones appeared in the form of capital productivity, capital intensity, and so on.
Today we will talk about cost as one of the most important (if not the most important) indicators of economic analysis of business performance. What is cost?

Types and types of cost
In fact, the cost price is the totality of all (I emphasize all) expenses in monetary terms from the beginning of the business process to its final completion.
Important - very often the cost price means exclusively the costs of producing one unit of product; at most, total costs are added to the total amount. Which is fundamentally wrong; in fact, this is only one part of the total cost and, ultimately, the total amount must also include costs associated with organizing the business process. That is why there are two main types of cost:
Total cost (average)- this is a complete list of expenses, including expenses associated with organizing the business itself and purchasing equipment. For convenience and to obtain a readable analysis, the total costs associated with creating the business itself, including the contribution of working capital, start-up capital, etc., are divided into an estimated payback period and added in equal parts to general production expenses, as well as depreciation of fixed assets. Thus, the average cost per unit of production is formed;
An example of calculating the total cost.
Start-up costs for starting a business are 1,000,000 rubles, including fixed assets and working capital (conditionally, the full payback period in the business plan is 60 months). Total 16,667 rubles per month.
General expenses (salaries of the director, cleaners, taxes, building rent, lawyer’s services, etc.) amount to 150,000 rubles per month.
1000 units of leather belts were produced in a month (). The total costs for production amounted to 500,000 rubles (cost of leather, electricity, wages for workers, paint, threads).
Total total cost will be - 16667+150000+500000 / 1000 (product units) = 667 rubles for one leather belt (calculations are conditional)
Marginal cost- such calculations are used to determine the break-even threshold for production, plus, of course, profit maximization. What does this mean? In fact, there are two main elements: total production costs, plus depreciation and start-up capital, and the second element is the cost of production itself (how much money we will spend if we produce a unit). So the first category is not directly related to production volumes (or rather, it is extremely elastic). By and large, a salesperson in a store can sell both (or) and 100.
Example of marginal cost calculation.
We take the numbers from the example above, but the calculation method changes:
1 month 1000 belts produced – 16667+150000+500000 / 1000 = 667 rubles
2 month 1500 belts produced - 666667+16667+150000+750000/2500 =633 rubles
3 month 1200 belts produced -1583334+16667+150000+600000/3700 = 635 rubles
As you can see, the marginal cost directly depends on the quantity of products produced and shows how effective it is to increase production in the future. Average reflects the current state of production, trade or provision of services.
There are a huge number of different types of cost, in fact, its type depends on the owner’s desire to control this or that area of work, the main classification looks like this:
- Shop price – this refers to the cost of individual sections of the production cycle. Transferring it to a small business, we can recall the production of fried sunflower seeds, where you can keep separate records of the cost of the frying process and separately the process of packaging the products;
- General business cost (or indirect) - this includes all expenses associated with managing and maintaining the business as a whole, things that are not directly related to the production process (for example, a cleaner or lawyer’s services, etc.).
- Production cost is the sum of workshop and general economic costs;
- Full cost - it is calculated as the sum of production and plus expenses associated with the promotion of goods (advertising, delivery, promotions, presentations), depreciation and, of course, start-up capital (in a proportional breakdown.
Cost structure for business
Regarding the cost structure, two main points can be distinguished:
- Firstly, there is the so-called net cost structure. This gradation is developed and maintained as a cumulative total of total expenses in individual areas (blocks or items). It can be noted that the gradation was developed for large businesses; for small individual entrepreneurs or LLCs such a complex system is not needed. True, for a full analysis and, especially, drawing up a business plan, it is worth using an expanded structure.
- Raw materials involved in the main production (activity) include materials, components, semi-finished products, units, components
- Energy costs - gasoline, diesel fuel, electricity, other types of fuel (in certain types of production this is one of the most significant expense items).
- Depreciation of fixed assets - equipment, machines, appliances, display cases, refrigerators, shelving.
- Salaries of key personnel, including mandatory payments and taxes
- General production expenses - wages of service personnel, advertising costs, office maintenance, and so on.
- Work of third-party organizations (contractors), outsourcing or simply contract agreements
- Administrative expenses - expenses for maintaining the management apparatus, paying taxes.
In addition, the cost price is accepted classify by elements of production costs, while a separate article or block may contain several different elements.
Main elements of cost price:
- costs associated with preparing production facilities and launching;
- costs reflecting investments in technology, production, management decisions;
- investments in the development of the scientific and technical base, development projects, research;
- costs reflecting the service component of the process of releasing goods;
- investments in improving working conditions;
- salary, vacation pay, social contributions;
- mandatory (insurance) payments (contributions);
- acquisition of fixed assets, depreciation;
- purchase of raw materials;
- other costs (including social costs, including “resolution of the issue”);

How to calculate your own cost
In fact, independently calculating the cost of a specific business is not difficult, but the trick, as always, is in the details:
- First, it is necessary to keep full records of activities, and this does not mean accounting for taxation (this was discussed in the article and), but namely economic activities. In Russia, accounting and, as a consequence, costing and tax accounting of costs are two different things.
- Secondly, cost accounting should be carried out by blocks, that is, costs of core activities and management costs (general). By the way, this also applies to costing for stores.
- Third, after summing up the overall results, that is, calculating how much was spent, it is imperative to transfer it in the context of sold or produced products. This will give you the opportunity to see the real profitability of the business. That is why when they say that the markup in trade is 100-150%, this absolutely does not mean that the profitability of the business is the same. If we remove from the markup the costs associated with selling products and defects (losses), the markup will decrease to 50-70%, alas, the costs in this business are high.
Ultimately, you will reach your real business profitability indicators, which is very important for any startup.
I often hear the question, how much is cost related to production volume?
There is no definite answer here; it all depends on how high the share of general business expenses is, that is, costs not directly related to production.
For example, if you have built your own greenhouse and grow cucumbers in it (which gives you the right not to pay taxes), then the level of general business costs will be minimal, you can even order that there will be no such costs at all. Accordingly, volumes practically do not affect the cost, another thing is when there is a company with staff, paying taxes, then in this case such an influence will be traced and the larger the production, the more noticeable this process.
That's all, if you have any questions, ask
Interesting on this topic
The release of any product (as well as the provision of a service) is associated with preliminary production investments. In modern economic theory, the totality of relevant types of costs is considered to be cost. What are the approaches of Russian economists to studying this phenomenon? What is cost in terms of business efficiency? What are the key conditions for its optimization?
Cost: theory
First, let's define what cost is. By this term, modern economists understand the financial expression of an enterprise’s expenses directly related to the production and sale of goods. The fact is that almost any production includes costs for raw materials, electricity, fuel, payment of labor compensation (and accompanying social obligations), depreciation reimbursement, etc. The firm's total costs are the total cost of its products.
Cost and profit
Reducing the corresponding costs of producing goods directly affects the organization's profit. The most important criterion here is to maintain the proper level of quality of the products produced. If it does not meet the current needs of consumers and clients, then demand will fall and problems with revenue will arise.
Thus, the cost calculation methods used by the company are extremely important criteria for business efficiency. Many economists consider it, however, not a quantitative, but a qualitative indicator. Cost, therefore, reflects the total range of resources that the company possesses.
Cost Components
What is cost in terms of the components that form it? Modern economists include the following types of costs:
- costs associated with preparing production facilities and putting them into operation;
- costs reflecting investments in the production of goods, the use of certain technologies, and the implementation of management decisions;
- costs associated with the company's investments in the development of the scientific and technical base, various kinds of development projects, and research;
- costs reflecting the service component of the process of releasing goods;
- investments in improving working conditions;
- salary, vacation pay, social contributions;
- insurance payments;
- acquisition of fixed assets, depreciation;
- purchase of raw materials.
Within a typical production structure, which product costs account for the largest share? This, as many economists believe, is precisely the purchase of raw materials and materials that are subject to further processing. In some industries, this expense item exceeds 80% of total costs. In a number of cases, the production cost of an enterprise includes moments when the factory is running “idle” (production defects, various types of technological downtime, etc.).
What is not included in the cost?
What, in turn, is not an integral part of the cost, based on modern economic theories? These components usually include, in particular, costs and lost profits associated with the implementation of projects suspended due to objective or independent of the will of the company management. Also, production costs, as a rule, do not include resources spent on servicing mothballed capacities.
The cost of releasing a product usually does not include costs associated with lawsuits, fines and other sanctions provided by law. Some economists also prefer not to include written-off or uncollectible receivables in the cost of production.
Classification of costs
The costs that form the cost of a product are usually classified into two categories. There are homogeneous cost components (they may include, for example, personnel salaries), and there are complex ones (they may reflect, in particular, the costs of purchasing equipment).

There are costs of a fixed nature, the value of which does not directly depend on the number of goods produced (including rent for premises), and there are variable costs, which, in turn, are proportional to the rate of production (purchase of raw materials, payment of personnel - new personnel are hired) .
Analytical aspect
How is product cost analysis carried out? Several key indicators are used. Among these, for example, is the cost estimate (total), the number of costs per one commodity unit, as well as per one ruble of products sold.
The first indicator reflects the total amount of costs recorded by the company in the course of using all types of production facilities, paying for related services (engineering, installation), and launching the production of new products. This figure can be divided by the number of units produced, and also be the basis for calculating a coefficient correlated with one ruble of the product’s selling price.

Cost components can be classified according to a number of other criteria. This may be the composition of costs (expenses for a specific area of the company’s activities - workshop, scientific department, retail, etc.), the duration of the period of use of funds (month, quarter, year and longer intervals), type of reporting (current , forecast, etc.).
Costing aspect
How is cost calculation carried out when the task is to calculate coefficients for specific expense items? That is, when the total indicator in the form of an estimate does not interest us, we need an analysis of costs relative to their specific purpose. Very simple.
First we define the calculation objects. These can be single products, product groups, and if we are interested in the cost of services, then we specify the types of services to be studied. Then we select the calculation criteria (as a rule, this is some kind of natural indicator - kilogram, meter, etc.), and they may not coincide in content with the object in the form of a single product. But this is completely normal - just the same, grouping individual goods, based on the equal applicability of calculation criteria, is much more convenient from the point of view of cost analysis than operating with individual units of production.
In any manufacturing company or organization in the service sector, there is a need to calculate production costs. In a competitive market, this value is an indicator of the economic balance and profitability of the business. The final price of the product or service depends on the values of this indicator. Next, let's look at this concept in more detail and learn how to calculate the cost of production.
Why is it important to know the cost of production?
The cost value is the total cost incurred by the company for the production and sale of products.
When talking about expenses, we mean funds allocated for the purchase of raw materials used in the manufacture of products, employee salaries, maintenance of logistics processes of delivery and warehouse, marketing efforts, as well as costs associated with ensuring the sale of goods.
Best article of the month
We have prepared an article that:
✩will show how tracking programs help protect a company from theft;
✩will tell you what managers actually do during working hours;
✩explains how to organize surveillance of employees so as not to break the law.
With the help of the proposed tools, you will be able to control managers without reducing motivation.
An uninitiated person may think that there is nothing complicated in costing. However, this feeling is deceptive. In any company, such an important operation is entrusted exclusively to professional accountants.
It is necessary to calculate the cost of products quite often. Basically, in enterprises this happens once every quarter, half year or year.
For any beginning entrepreneur, it is very important to calculate the cost of his products or services at the starting stage, otherwise it will be impossible to determine the margin, payback period and other important indicators of the economic efficiency of the business.
What elements make up the structure of production costs?
The conditions of production, logistics, marketing and sales at different enterprises can differ radically from each other. For example, the business processes in a food distribution company and in an online cell phone store are completely different. For this reason, each individual company calculates the cost of products or services specifically for itself, which would be impossible if it did not have such a flexible structure.
Cost is the sum of costs that can be classified:
- costs of purchasing raw materials and supplies;
- spending on fuels and lubricants;
- costs associated with the maintenance, operation and repair of machinery and equipment;
- remuneration of personnel, as well as contributions to the social insurance fund, compulsory health insurance and pension fund;
- space rental, marketing promotion efforts, etc.;
- costs for various promotions in socially responsible businesses;
- depreciation of machinery and equipment, buildings and structures, etc.;
- management costs;
- fulfillment of obligations under service contracts with contractors, for example, payment for the installation of an air conditioner in a production facility.
For each type of expense, you can set the share in the total amount of expenses. In this way, bottlenecks in the organization’s business processes can be identified.
The main cost component does not include lost profits or expenses incurred as a result of the freezing of one or more company projects through no fault of its management. It also does not include the costs of maintaining unused/suspended enterprise facilities.
The costs of legal proceedings and payment of fines are also not included in the cost structure of products. Also, some accounting experts believe that bad receivables should not be taken into account when calculating this parameter.
The cost of a product or service is a flexible and changeable structure, not only in terms of the variability of its components, but also in terms of its value. It depends on certain phenomena in the economy and aspects of the company itself, such as:
- inflation;
- interest rates on loans;
- location of the enterprise's physical assets;
- level of competition;
- degree of automation and mechanization at the enterprise, etc.
Incorrectly calculated unit cost of production can lead to financial losses and even the closure of the organization.
Types of production costs
There are several types of production costs.
- Full- includes the amount of all costs, including funds spent on own production and the purchase of machinery and equipment. It is also called average cost.
The costs of organizing business activities are usually distributed over certain calendar periods according to their expected payback period. Over time, these costs are included in production overhead. If their value for a certain period is divided by the number of units of manufactured products, we get the average cost of one unit.
- Limit- is directly proportional to the volume of production of goods and shows the price of the next additionally produced unit. Based on data on this parameter, one can judge the feasibility of increasing production volumes.
The following classification of cost is based on the desires of enterprise owners to focus on optimizing costs in a certain area of business:
- Shop cost - contains the totality of costs incurred by all divisions of the company in the process of releasing new products.
- Production- a set of shop costs, general and target costs.
- General economic- contains organizational expenses that are indirectly related to the direct production of products.
When planning and calculating, standard and actual costs are distinguished.
To isolate the actual cost of a product from its final price, the accountant is guided by current cost indicators. This method is imperfect, since very often there is a need to calculate the cost of a unit of goods even before the sales department sells it. And it is necessary to know it in order to understand the degree of economic efficiency of entrepreneurial activity.
When calculating the standard cost indicator, they are based on the values of established standards in the finished product production department. With the help of this production costing method, company management can effectively manage the consumption of raw materials. This, in turn, has a positive effect on the financial condition of the organization and reduces the risk of ineffective use of its budget.
Calculation of production costs: basic methods
There are two tools to calculate the cost of manufacturing one unit of a product: costing and tiering. As a rule, the first approach is used. This method is capable of providing prompt and accurate data.
Cost calculation- this is the determination of the cost per unit of goods produced. During the calculations, costs are classified and distributed among various items.
Based on the organization’s business processes, cost calculation is carried out in the following ways:
- Direct costing. This is an accounting tool in which the accountant operates on the value of direct costs, while writing off indirect costs through sales. Thus, a limited cost is determined.
- Custom method. When using this method, the cost of a single unit of goods is calculated. This type of costing is used in the manufacture of unique products in one single copy. For this type of production, it is most effective to use this method. Examples include the production of yachts, in particular, or the production of premium cars to order.
- Transverse method. This method is used for mass production of products, in which the technological process is divided into several stages. For each specific stage of production, the cost is calculated separately. An example in this case is the production of bakery products: at the first stage the dough is made, at the second the products themselves are baked, at the third the products are packaged.
- Process method. This method is used in the mining industry, as well as when the production process is based on one simple technology.
Example of calculating production costs
Typically, production costs are calculated using 3, 6 or 12 months.
This parameter is calculated for the final product over a certain time period in the following way:
- We add up the amounts spent on the purchase of raw materials and materials. This takes into account all the raw materials processed and used at various stages of production of the final product.
- We calculate how much finance was spent on fuels and lubricants.
- Let's sum up the costs of paying staff and contributions to funds.
- We add up the depreciation values and other costs for maintaining and operating machinery and equipment.
- The amount of costs incurred in the process of direct sales of products.
- Other funds directly or indirectly aimed at the production of goods.
Example calculating the cost of rolled metal for one thousand linear meters of products and setting the price for 1 m of the final product:
- purchase of raw materials and materials - 30,000 rubles;
- fuel/electricity consumption - 15,000 rubles;
- staff wage fund - 20,000 rubles;
- mandatory deductions - 40%;
- general business expenses - 20% of the payroll;
- general production costs - 10% of the payroll;
- packaging costs - 5% of general production costs per thousand linear meters of rolled products;
- production profitability -15%.
We determine how much was spent according to paragraphs 4, 5 and 6 of the source data:
- 20,000 x 40 / 100 = 8,000 rubles. - contributed to funds based on wages;
- 20,000 x 10 / 100 = 2,000 rubles. - general production expenses;
- 20,000 x 20 / 100 = 4,000 rubles. - general business expenses.
In this case cost of manufacturing one thousand linear meters of rolled steel is calculated as follows:
30,000 + 15,000 + 20,000 + 8,000 + 2,000 + 4,000 = 79,000 rub.
Costs for selling goods:
79,000 x 5/100 = 3,950 rubles.
To calculate the total cost of one thousand linear meters of rental, you need to add up the cost of production and the cost of selling products:
79,000 + 3,950 = 82,950 rub.
From this we conclude that total cost of one rental meter is 80 rub. 30 kopecks
Final product price, taking into account profitability:
80.3 + (80.3 x 15 / 100) = 90.5 rub.
Extra charge in the price structure of one linear meter of product:
80.3 x 15 / 100 = 10.2 rubles.
Calculation of total cost(PST) is produced according to the following formula:
PST = MO + MV + PF + TR + A + E + ZO + ZD + OSS + CR + ZR + NR + RS
- MO - the total cost of purchasing basic materials;
- MV - the total cost of purchasing related materials;
- PF - the total cost of purchasing semi-finished products;
- TR - logistics costs;
- A - depreciation;
- E - cost of fuel and lubricants and electricity;
- ZO - personnel wages;
- ZD - staff bonuses;
- OSS - contributions to funds;
- ZR - plant costs;
- CR - shop costs;
- HP - non-production costs;
- RS - costs of selling products.
Cost items are set depending on the type of final product. This value will be the total cost incurred by the business in the production and sale of the final product, that is, the full cost of each unit of goods. Adding profit to it, we get the price of the final product.
Expert opinion
What mistakes are made when calculating costs?
Elena Breslav,
Director, consulting company Business Matrix, Riga
As practice shows, when calculating the cost of production, a large number of inaccuracies are allowed - one can even say that so many mistakes are not made when solving any other economic issue. All these errors are conditionally divided into two categories:
- meaningful arising from the incorrect choice of any cost or volume indicators;
- settlement(or appeared by chance).
Another large category consists of errors in incorrect selection of the distribution base. They also differ depending on whether it is technically possible to take the correct base. If there is such a chance, then the conversation will focus on the economist’s low qualifications - in cases where turnover is used instead of marginal income or marginal income instead of the period of service provision. In practice, you can also encounter mixed situations (see Mixed distribution base).
There are also situations when, according to one cost distribution base, a product is highly profitable, but not according to another.
If we talk about calculation errors, they are common, varied and unpredictable.
How is production cost recorded at an enterprise?
It is quite difficult to take into account the first cost of a product. This procedure involves the use of a wide range of possibilities, including a statistical method for analyzing the production process. This must be done in order to create a list of expenses without which production of products is impossible. Also, to optimize their use, appropriate standards for raw materials are formed.
A key part of production costs is raw materials. In this regard, accounting for production costs and costing focuses its attention precisely on this element, which forms the main part of the price of goods. There are three types of accounting methods:
- document flow;
- carrying out inventory;
- production line workflow assessment.
The first method establishes by recording the following points: standards for the use of raw materials, possible errors, that is, deviations from a fixed value at the time of production. There are situations when documentation displays conditions that allow consumption outside the established standards or prohibit it altogether. In order to optimize product output, it is often prescribed what the potential is for replacing one type of raw material with another.
Inventory is a procedure that is carried out to calculate the available volumes of raw materials and resources. It is performed systematically with a certain time interval (day, one shift, one week, one month, etc.). The required interval is determined by the organization’s specialists.
Production Line Efficiency Analysis- complements the documentation method. During such a study, not only the level of lag from fixed norms is discussed, but also the reasons why it happened are considered.
During the elimination process, it is established target- resolve identified problems with increased costs. This helps reduce the cost of goods.
In what areas is production cost analysis carried out?
1. Analysis of product costs by cost elements and costing items.
The production costs of enterprises in planning, accounting, reporting and analysis are combined in two directions: economic elements and costing items.
- Cost analysis by element.
Combining costs by element is integral and mandatory and is determined by the Regulations on the composition of costs. This grouping reflects what exactly was consumed during the production process, what is the ratio of individual components to the total cost. But it should be remembered that only purchased materials, semi-finished products, fuel and energy are displayed for the components of material costs. Wages and social contributions are taken into account only in relation to employees of the main activity.
Grouping expenses by element provides a chance to control the formation, structure and dynamics of expenses by type that characterize their economic content. This is necessary in order to consider the relationship between living and past labor, rationing and research of inventories, the calculation of partial indicators of turnover of certain types of regulated working capital, for other calculations at the sectoral, national and national economic levels (for example, to determine the amount of national income created in industry) .
The element-by-element consumption of all material, fuel and energy resources is used to establish material expenditure plans and evaluate its implementation. Such an analysis makes it possible to determine the key areas for searching for reserves depending on the level of material intensity, labor costs and the volume of warehouse space of the enterprise.
- Analysis of the cost of production of an enterprise's products based on costing items.
The standard grouping of costs by costing items is established by the Basic Provisions for Planning, Accounting and Calculation of Production Costs at Industrial Enterprises. The itemized display of expenses in planning, accounting, reporting and analysis reveals their intended purpose and connection with the work process in production. This grouping is used to determine costs for individual types of goods produced and the place of their origin (shops, sections, teams).
2. Analysis of costs per ruble of commercial products.
In almost all areas of industrial production, the cost target is fixed by the organization in the form of a maximum level of expenses per one ruble of marketable products.
This indicator characterizes the level of cost of the ruble of an impersonal product. It is calculated as the quotient of dividing the total cost of production by its price in the company's wholesale purchases. This indicator can be called the most general, since it reflects the direct relationship between the cost of production and the profit received from its sale. Also, the advantages of this criterion are dynamism and wide comparability.
Deviations in four factors that are in direct functional connection with this indicator have a direct impact on changes in the level of expenses per ruble of marketable products:
- structure of the goods produced;
- the level of costs for the production of certain products;
- pricing policy and tariffs for consumed material resources;
- wholesale cost of manufactured goods.
3. Analysis of the influence of direct material costs on the cost of production at the enterprise.
The key goals of analyzing material costs as one of the main components of the cost of goods are:
- finding and measuring the impact of certain groups of factors on the deviation of expenses from the established plan and their change in relation to similar previous periods;
- identifying reserves for saving material costs and ways to optimize them.
In the course of studying the reasons for the deviation of material costs from the similar planned previous period and other time periods without comparison, these reasons are conventionally called factors of cost, standards and replacement. Cost factors are changes in the price of raw materials and materials necessary for the production of products, as well as the deviation of real costs per unit of goods from the norm established in production. The replacement factor is the complete replacement of one type of material with another or adjustment of the composition of the mixtures used and the content of useful elements in them (this example is especially widely used in the food industry).
The methods of analysis for determining these groups of factors are identical for all items of material costs, that is, for raw materials and basic materials, fuel, purchased semi-finished products and components.
4. Analysis of the impact of labor costs on the cost of main production.
The wages of an enterprise's employees are a key component of the cost of production of goods; It is especially important in the mining industry and mechanical engineering due to its high specific gravity. Only remuneration for production employees is included in the cost of production as an independent column. The wages of other groups of industrial production specialists are included in complex items of production costs, as well as transport and procurement costs. Salaries and bonuses of employees involved in auxiliary processes are included in the cost of resources (steam, water, electricity) and affect the cost of production through those complex items that contain costs for resources.
Compliance with the production plan directly or indirectly determines the remuneration of personnel working on a piece-rate basis and bonuses paid from the wage fund (bonuses accrued from the consumption fund do not affect the wage fund). Other components of the salary fund are determined by the number of specialists, tariff rates and salaries of workers, that is, they are influenced by a large number of common factors. In this regard, the analysis of remuneration is carried out in two directions: assessing the salary fund as an element of production costs and considering wages in the context of individual calculation items, primarily an independent item - the earnings of production employees.
Only after common factors have been discovered, due to which there was a deviation in the wage fund of certain groups of workers, is it revealed to what extent they influenced different parts of the cost of goods.
5. Analysis of complex production cost items.
Comprehensive costs include several elements. The cost includes the following groups of complex costs: for the preparation and development of the release of new product lines, for the maintenance of the enterprise and its management (maintenance and operation of technical equipment, workshop and general expenses), the percentage of defective products, other production and non-production (commercial) costs .
Each item includes complex expenses of various economic nature and purpose. In accounting for production costs, they are detailed into more fractional items that combine costs of the same purpose. In this regard, the deviation from the cost estimate is determined not by the item as a whole, but by the independent columns included in it. After this, the amounts exceeding the plan for some items and savings for others are calculated separately. When assessing the changes obtained, one should take into account the dependence of some costs on the plan for production volume and the number of employees, as well as on other conditions of the industrial process.
Based on their dependence on the volume of production, costs are divided into those that do not depend on the degree of implementation of the plan - conditionally constant - and dependent - variables. Variable costs can also be divided into conditionally proportional, which, when the production plan is exceeded, increase almost in full accordance with the scale of the achieved indicators, and digressive, the growth of which to one degree or another lags behind the above-plan increase in production volume.
As practice shows, with minor deviations of the production level from the plan (within ± 5%), workshop and general plant costs remain unchanged.
Expert opinion
Is it possible to sell a product at a price below cost?
Ekaterina Shestakova,
General Director, Current Management, Moscow
Selling products at a price below cost can be due to a large number of different reasons: the desire to attract new customers, expand sales markets through price dumping, the desire to win a government contract, the last chance to earn financial resources in situations where the enterprise is on the verge of bankruptcy, in some In cases, this is simply the expiration of the product's shelf life. When used correctly, dumping as a business tool can be useful, but you should weigh the possible risks.
From one position, selling products at a price below their cost can be interpreted as unfair competition, but on the other hand, both the end buyer, who purchases the product at a low price, and the seller, as they can attract potential customers and sell an illiquid product, benefit.
In some situations, selling a product at a price below cost is equated to dumping, although this term in English means dumping, that is, dumping is the sale of products/services at a throwaway price.
Selling a product at a price below cost does not in all situations have a connection with the desire to suppress the position occupied by a competitive company or increase sales volume. For example, transactions with signs of understatement of the tax base. Often, importers sell products at a price lower than the invoice price provided by the exporter. Such a system is used for tax optimization and requires the parties to have confidence in each other and the absence of interrelationships - family relationships, participation of one company in another by more than twenty-five percent, etc. If such a transaction was carried out between mutually dependent participants, then additional charges are possible taxes, application of penalties and interest.
One of the popular types of selling goods below their cost is selling off inventory for various reasons. For example, the volume of production of an enterprise exceeds the capacity of the domestic market. In such a situation, the company is faced with the question: either not to use production at full capacity and not produce products, or to release them and sell them at a lower cost. In other conditions, the organization wants to attract a larger number of customers and expects that in addition to products sold at a price below cost, they will also buy other goods.
Also popular is the method of reducing the cost of the main product while simultaneously increasing prices for additional services and related assortment. At the same time, an advertising campaign is organized with announcements of discounts. But in this situation, financial results will directly depend on the ability of sales managers to impose additional services or related products on customers.
Sales below cost can also be carried out for reasons stated in Article 40 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, and be associated with seasonal and other changes in consumer demand for products/services, with the loss of the required level of quality or other consumer properties of the product, or with the expiration of the shelf life.
When using these types of occasional sales, it is necessary to identify assortment with low demand, as well as set the discount amount and record the sales procedure in the company’s local documentation (for example, in the marketing policy regulations). Equal conditions must be determined for all clients; otherwise, government inspection authorities may have questions for the company.
Sales of products below production costs can be aimed at ousting competing companies from the market and subsequent fixation of the monopoly value of goods.
What methods can be used to reduce production costs?
There are ways in which the costs that affect price can be significantly reduced. This can be realistically accomplished by conducting a detailed study of the total cost, all costs of production. And in such a situation, you can plan to take measures to reduce the cost of the product and calculate its optimal price.
Before deciding to reduce prices, consider the following points:
- Profitability. If the organization’s product is not profitable, then discounts will transfer it to the category of unprofitable ones. In this situation, there is no point in increasing turnover, since this will only lead to an increase in costs. It would be more logical to reduce sales volumes for 2-3 months and during this period find ways to reduce the cost of production.
- Revenue per employee per year. This is a fairly average parameter, but it shows whether there is movement in the company in the direction of increasing efficiency. If revenue decreases, this means that a large number of operations in the organization require optimization, and there are also large indirect costs. An increase in sales turnover will only bring an additional decrease in the profitability of the product and the company's profit. The best option in this situation would be to start reducing costs and increasing the efficiency of business processes in the enterprise.
- Assets. In a situation where an office building, workshop, warehouses and other assets are not the property of the organization, then you can abandon some areas, concentrate on a smaller area or move to more affordable premises. If the property belongs to a company, then the available capacities should be used to the maximum in order to obtain a marginal profit to cover the costs of their maintenance.
- Purchase cost. If your organization is a significant client for the main supplier companies, then try to negotiate additional bonuses and discounts for increasing purchase volumes. If the contractor refuses you this, then there is no point in purchasing from him in large quantities; it is easier to find new contractors (accepting a temporary decrease in sales volume).
- Accounts receivable and warehouse inventories. These are two types of assets in which the organization's financial resources are frozen. If the situation is such that the larger volumes you ship goods, the less money you receive, then it is better to ship less, but have high turnover and liquidity.
If the research was carried out competently and taking into account all the factors required for an objective assessment, then there are all the prerequisites for establishing the process of producing goods.
According to experts, one of the most effective methods of reducing production costs is increasing labor productivity.
Labor productivity- this is the amount of work completed for a specific amount of labor in a certain time.
This parameter is affected by the following factors:
- The level of professionalism of the personnel involved in the product creation process. It is more profitable to exchange untrained employees with low qualifications for masters of their craft. This will help you reduce the number of personnel involved in the production process, thus reducing wage costs, which also have an impact on the cost of goods.
- Production conditions and organization of work space. At an enterprise that has modern high-tech equipment, energy costs will be much lower than at one that uses old mechanization. In addition, advanced equipment helps to reduce the volume of defective products, therefore, the costs of raw materials and materials used in the production process will also be reduced.
Another method to reduce the cost of goods is a technique, the essence of which is to cooperate and expand the specialization of production. This will help reduce expenses on management, administrative and other aspects of the organization’s activities.
Also, a method such as research, making the necessary adjustments and improving the way the company's key assets are used will help reduce production costs.
It is also possible to make changes to the leadership structure and management staff in the direction of reducing the number of employees. Since the costs of the company’s administrative activities also affect the cost of production and are taken into account in its calculations, reducing personnel and replacing quantity with quality will also lead to a reduction in costs and a decrease in this parameter.
Expert opinion
Four steps to help reduce costs
Zoya Strelkova,
Head of the “Company Economics” department of the group of companies “Training Institute - ARB Pro”, Moscow
Stage 1. Splitting the cost of the product into its constituent parts.
At the very beginning, it is necessary to isolate all the components of production costs and understand what influences their size.
Trading company. The maximum impact on the cost of products for the resale process is:
- the price of purchasing the goods from the supplier organization;
- trade and purchasing expenses (for delivery of products, customs duties, etc.);
- expenses for warehouse operations (packing, labeling of goods, etc.).
Manufacturing enterprise. The maximum impact on the cost of goods is:
- the price of raw materials, consumables and components used in the production process of the product;
- direct labor costs, that is, those that are directly related to product output;
- financial costs for electricity, water and other resources necessary in the process of manufacturing the goods;
- production outsourcing costs.
Organization providing services. The cost of the service is affected by:
- the price of materials used in the provision of services;
- direct labor costs;
- cost of services of other companies, for example, costs of transport, rent, etc.
Project organization. The maximum impact on the cost of projects is exerted by:
- the price of materials required to implement the project;
- direct labor costs;
- travel expenses;
- the cost of technical equipment required to implement the project;
- expenses for the services of other companies hired to implement the project (for example, performing the necessary examinations, paying for transport services, etc.).
These lists of financial costs are not exhaustive and may vary for different products. It is necessary to pay attention to the fact that the cost of production does not include administrative and general production costs. Costs that do not relate to specific products (accounting department salaries or warehouse lighting costs) must be calculated separately. O.
Stage 2. Search for factors that influence production costs.
At this stage, it is necessary to determine the internal and external conditions that affect each of the elements of production cost. Example: external factors include exchange rates, the level of quality of raw materials used in the industrial process, the required number of specialists in the company, etc. Internal factors include the presence of controlled organizations, disadvantages in the technology used in production, technical condition of equipment, etc.
Stage 3. Appointment of responsible employees for optimizing production costs.
After determining the factors that determine the cost of production of a product (service), optimization can begin. It is necessary to appoint responsible employees for improving performance for each identified criterion. For example, instruct the purchasing manager to collect all information on transactions with current and potential suppliers (discuss the possibility of obtaining discounts and deferred payments). The logistics department must immerse itself in research into new routes and modes of transport. Technologists and production specialists need to investigate all existing types of losses arising from the processing and storage of goods. Each specialist may be responsible for several issues. The employee must collect the necessary information and propose possible options for action: what exactly and how needs to be changed in the enterprise’s work process in order to reduce the percentage of losses and improve the current situation.
Stage 4. Establish systematic management of production costs.
First of all, it is necessary to change management accounting. You will need reports not only in finance, but also in physical units (kilograms, seconds, hours, etc.). Only then will it be possible to talk about what exactly influenced the cost: an increase in the purchase price or an increase in expenses. This matters because the actions and responsible employees in such a situation will be different. For example, your purchasing managers have ensured the cost is low, but storage conditions are still such that most of the raw materials are wasted. Thus, management's attention shifts to the logistics department.
Having created a detailed cost accounting, you will have the opportunity to manage its dynamics, since now it represents a set of elements that is understandable to you. What follows is a joint work process between several departments of the company, which should be led by the financial director, as he tracks all the numbers in the company. It is important that your control over cost management is not one-time, but systematic: as practice shows, the parameters monitored by the general director every week improve on their own. In addition, it is easier for you to influence the situation than for managers and mid-level employees. If negotiations between the procurement specialist and the supplier are not moving forward, chances are that one phone call or meeting will solve the problem.
The first results can be obtained within 3 months - six months. Everything will depend on proper organization and timing of certain actions, for example:
- collecting and researching information about the current state of affairs can last 2–3 weeks. In this situation, everything will depend on how the company kept records;
- searching for suppliers, comparing conditions – also takes 2–3 weeks;
- processing and discussing all information, drawing up a plan for further steps – 1–2 weeks;
- signing the developed action plan – 1 week;
- negotiations and conclusion of contracts with suppliers – 4–6 weeks;
- transition to new workflow schemes – from two to three weeks.
But you can start developing ideas based on the information collected as soon as you identify the factors that have an impact on the cost of production.
Expert opinion
Reducing costs through mechanization
Artem Kogdanin,
Director of LEDEL company, Kazan
Every company manager who knows how to calculate financial resources is aware that production based on manual labor will entail high costs, low quality of work and high risks associated with finding the necessary specialists. In connection with these points, the mechanization of operations performed manually at our enterprise occurs systematically.
Such use of technology is not in all cases justified from an economic point of view. In order to select work processes during which it would actually be more logical to abandon manual labor, we apply 2 criteria:
- Rejection rate. The most difficult operation in our company is mounting the board (the base for the lamps), since it is necessary to connect 120 components, the actual size of which in some cases does not exceed 0.5 millimeters, with an accuracy of hundredths. The cost of defects in this operation can be expensive. Previously, quality control departments had up to thirty percent of defective drivers (power supply with current stabilization and protection against voltage surges). Thus, due to such a large percentage of defective products, the final cost of manufacturing a given part increased by one third. It was simply unrealistic to reduce production costs by at least fifteen percent without using automation of manual labor. It was clear to everyone that this operation needed to be automated first and foremost. As a result, the share of defective goods in this area decreased to 5%.
- The time during which the operation is performed. Once every six months we make calculations of how many man-hours are needed to carry out specific actions and produce the lamp as a whole. The process is as follows: two-thirds of the team assembles about a hundred lamps; based on the best result, we calculate the standard man-hours. Example: if two workers assemble one lamp in thirty minutes, in total we get one man-hour, if four employees - two hours. We select operations that require the maximum amount of time; they are the ones that need to be automated first.
Naturally, not all processes require equipment with mechanisms. In order to give a competent assessment of this step, it is necessary to calculate the return on investment of innovations. I’ll tell you about this using our production as an example: at the moment, the driver is filled with electrically insulating polymer resin using manual labor. This procedure lasts approximately 5 minutes. The human factor accounts for 0.1% of defects. Once we decided to purchase a specialized mixer with a dispenser - you just need to bring a lamp to it and it will independently pour the required amount of substance. And such an operation takes only a few seconds. 5 minutes of employee work are estimated at approximately twelve rubles. The cost of resin for the production of one lamp is 150 rubles. And the device costs 500,000 rubles. When calculating the payback, we remember that the current defect rate is reduced, and the use of resin becomes more rational, since employees often forget it in containers. By reducing resin losses by twenty percent, we can save 30 rubles. from the production of each lamp. As a result, the benefit will be forty-two rubles (30 rubles + 12 rubles). In order to recoup the cost of a specialized mixer with a dispenser, we need to produce approximately 12,000 drivers (500,000 rubles: 42 rubles), and we produce this volume of production in one month.
Based on the experience of our company, I can give you the following advice on how to reduce the share of manual labor in production:
- estimate the labor costs for manufacturing the product- for this it is necessary to break the entire production process into separate stages;
- record all operations, measure the time required to complete them(this can be tracked even through CCTV cameras);
- calculate the cost of each operation, select the most expensive ones;
- find ways to reduce their costs.
Information about the experts
Elena Breslav, director, consulting company Business Matrix, Riga, consultant in the field of economics and enterprise finance. Author of the book “Budgeting: Step by Step” (co-authored with consultants of the Intalev company) and more than 100 scientific and journalistic articles. Candidate of Economic Sciences. The Business Matrix company provides services in the field of management consulting and offers proprietary training programs for senior managers.
Ekaterina Shestakova, General Director, “Current Management”, Moscow. Ekaterina Shestakova has a higher legal and economic education, a candidate of legal sciences, teaches at the Peoples' Friendship University of Russia, and is the author of books on tax planning. Work experience: from 2000 to 2008 - subordinate organizations of the Russian Ministry of Foreign Affairs, in 2008–2009 - head of the taxation group (branch of the Federal State Unitary Enterprise Russian Post), since 2010 - general director of Actual Management LLC. “Actual Management” specializes in tax consulting, legal services, and accounting. Year of creation - 2010. Staff - five employees.
Zoya Strelkova, head of the “Company Economics” department of the group of companies “Training Institute - ARB Pro”, Moscow. Zoya Strelkova graduated from St. Petersburg State Technical University. Specializes in diagnosing the economic condition of enterprises, auditing and modernizing management accounting of companies, developing economic business models for strategic planning projects. Participated in the implementation of strategic planning projects for enterprises in various industries. Author and developer of the Profit Interruptions & Losses approach (“Strategicity of everyday life. PIL approach”). GC "Training Institute - ARB Pro". Field of activity: strategic management and planning, business training, HR consulting. Territory: head office - in St. Petersburg, representative offices - in Moscow, Yekaterinburg, Nizhny Novgorod, Chelyabinsk. Number of staff: 70. Main clients: Synergy University, Sberbank of Russia, Gazprom, Irkutskenergo, Coca-Cola, etc.
Artem Kogdanin, director of LEDEL company, Kazan. The LEDEL® company was founded in 2007, and today is one of the leading developers and manufacturers of LED lamps in Russia and Eastern Europe.
